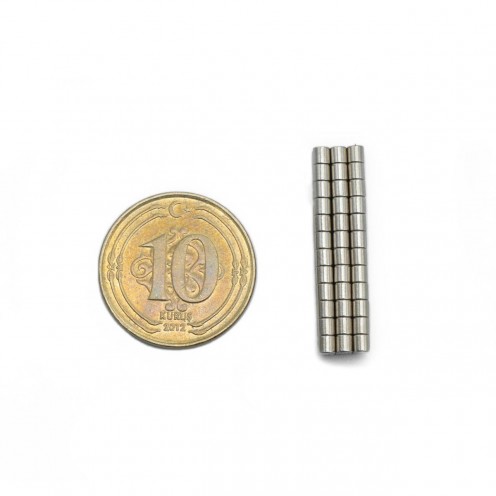
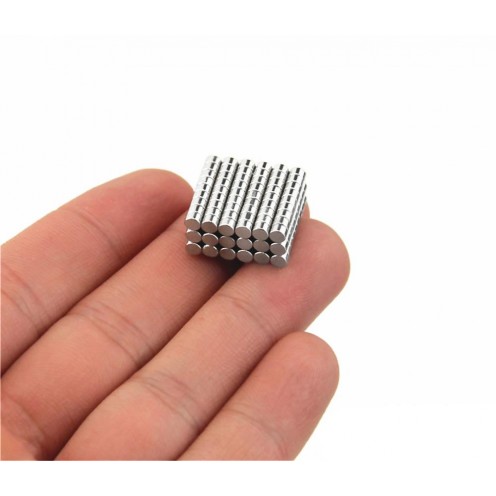
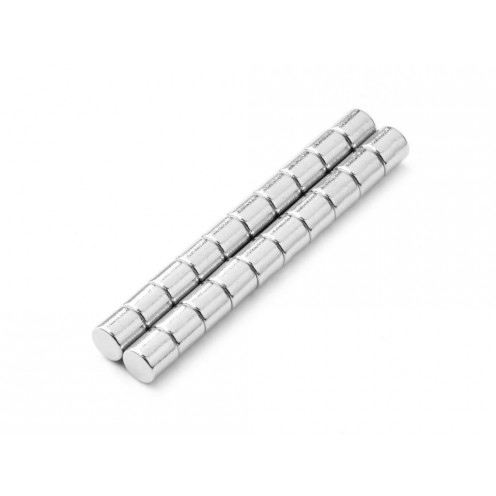
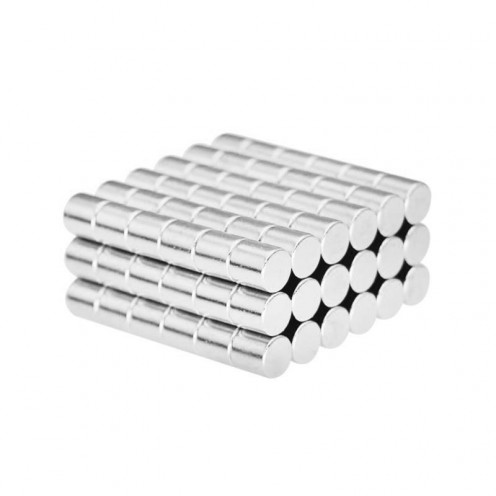
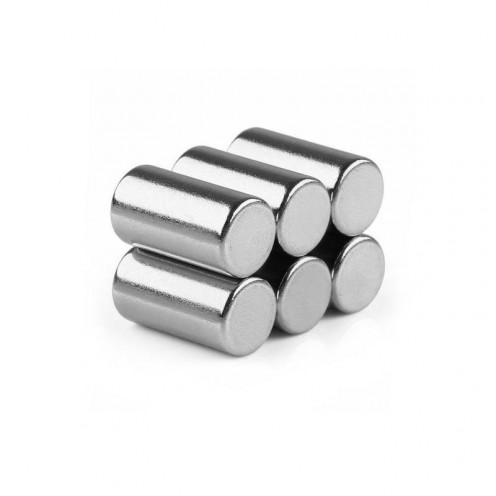
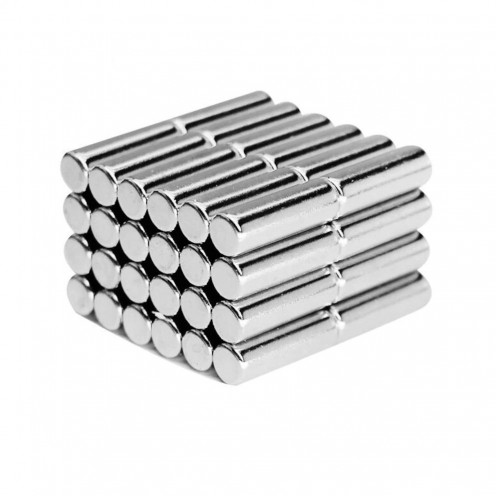
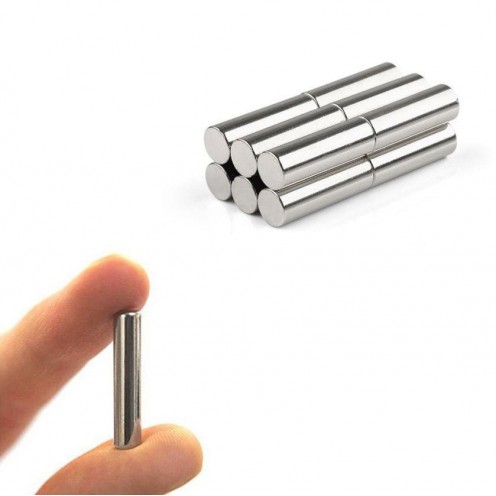
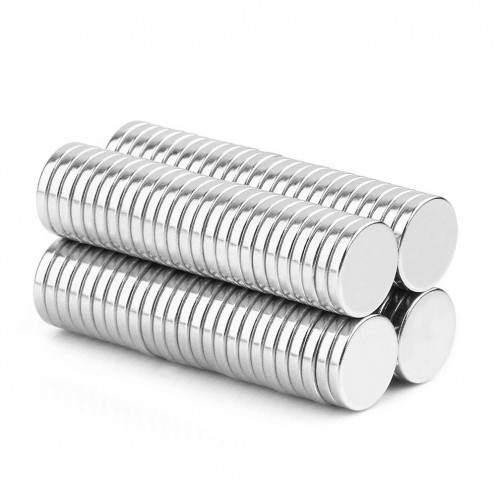
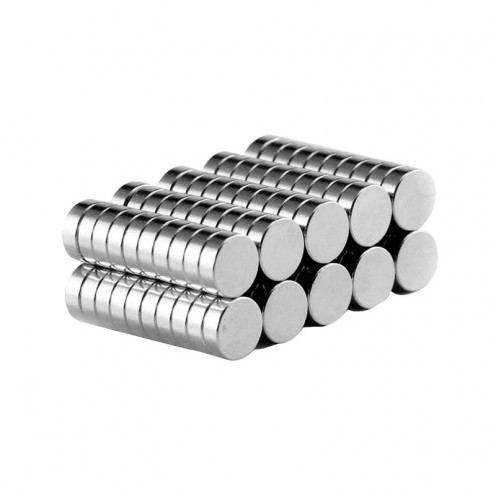
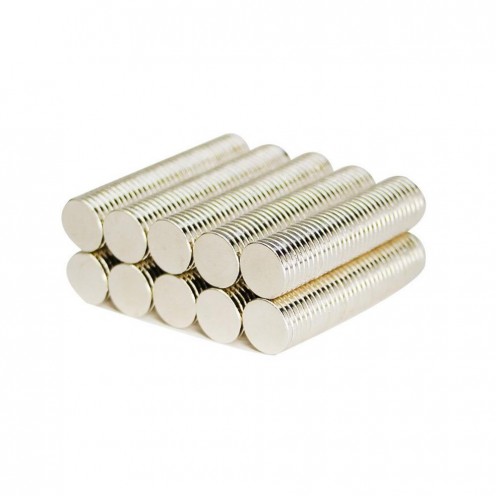
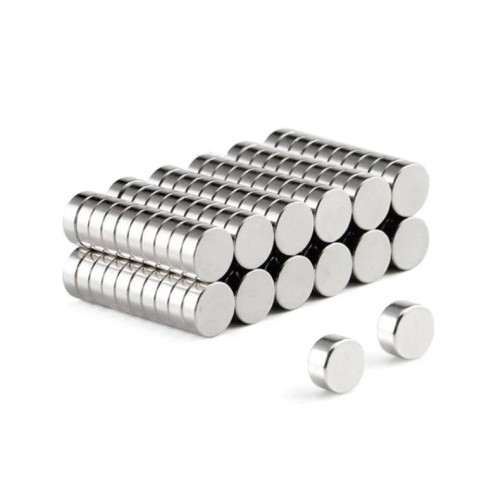
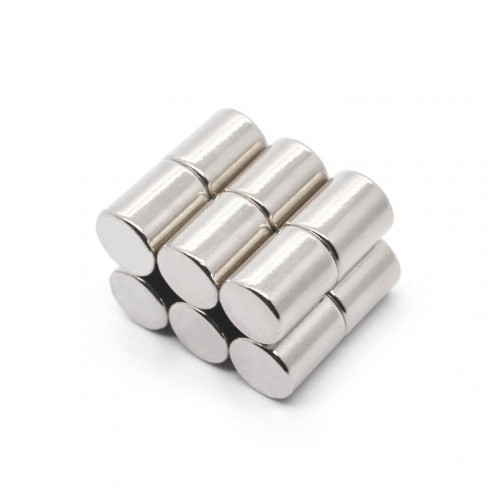
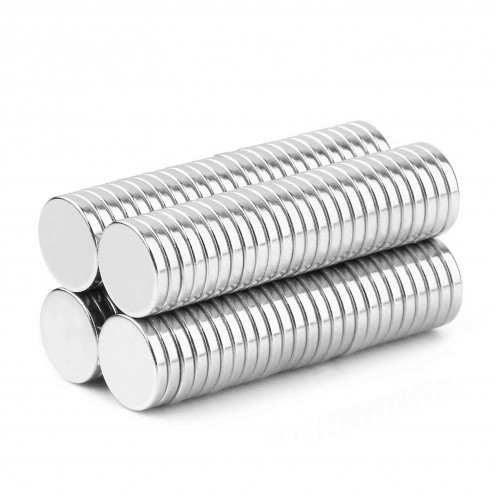
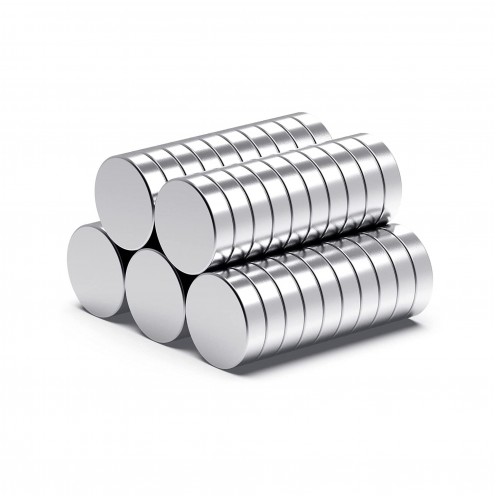
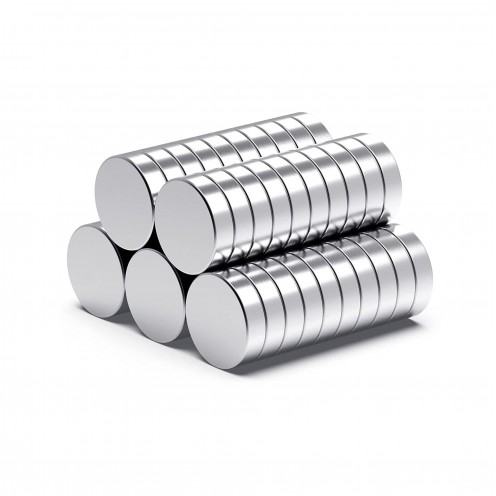
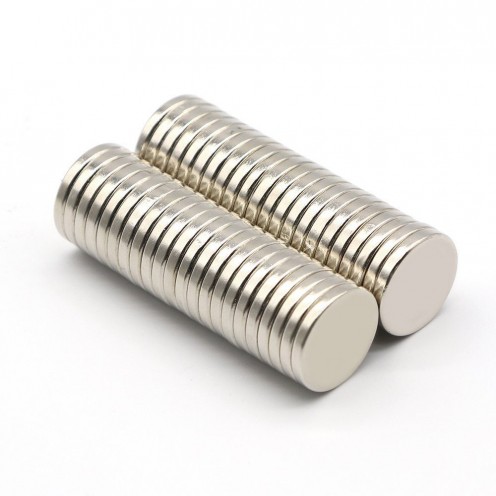
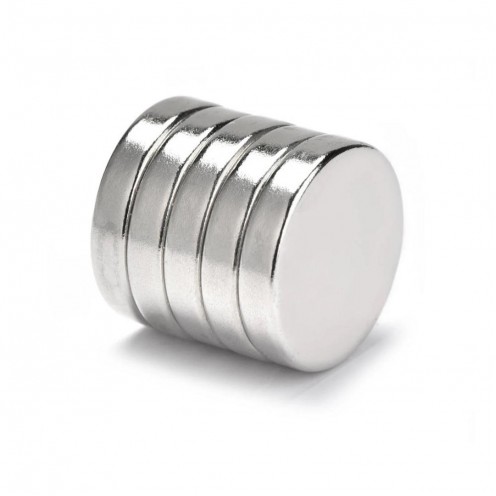
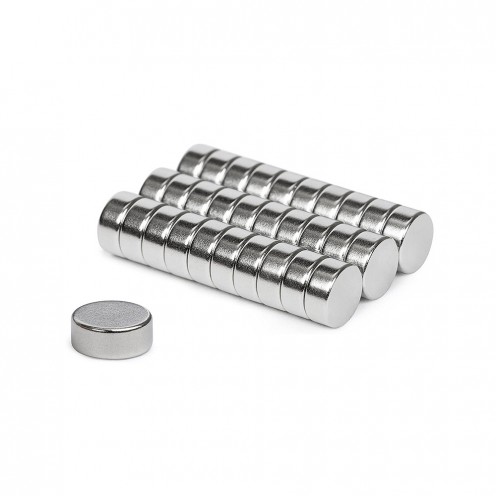
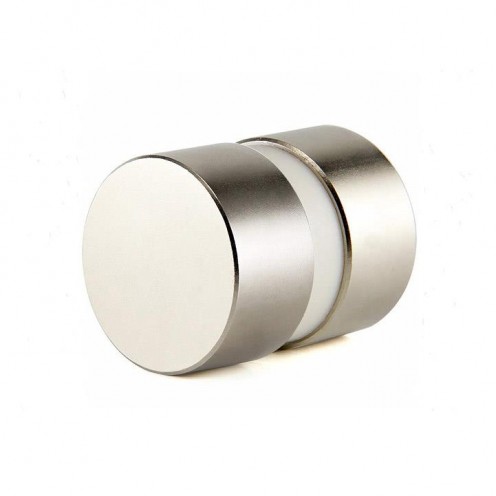
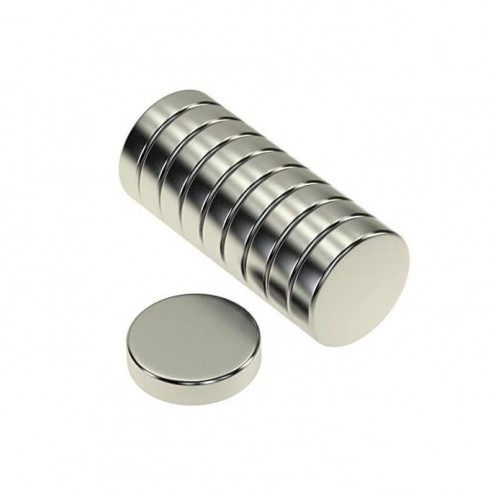
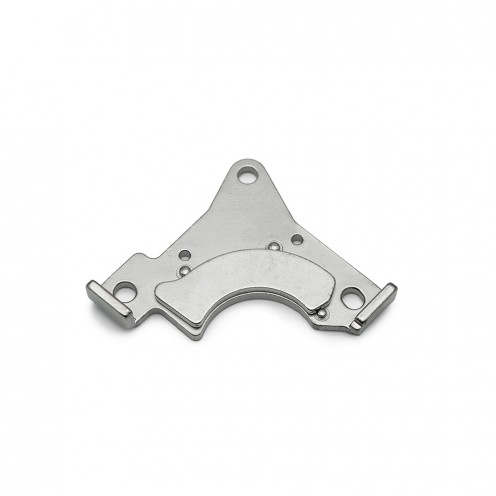
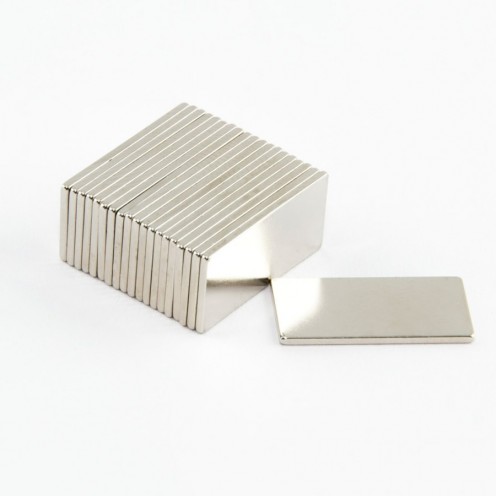
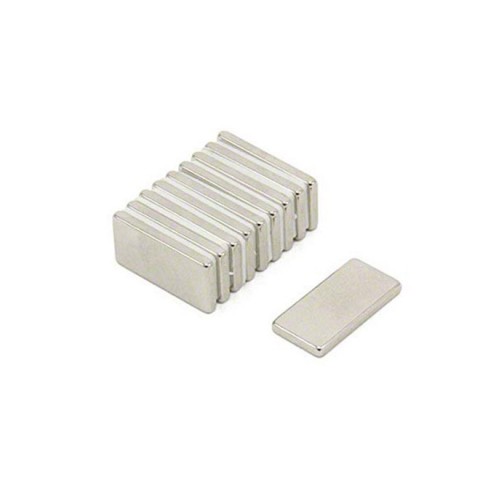
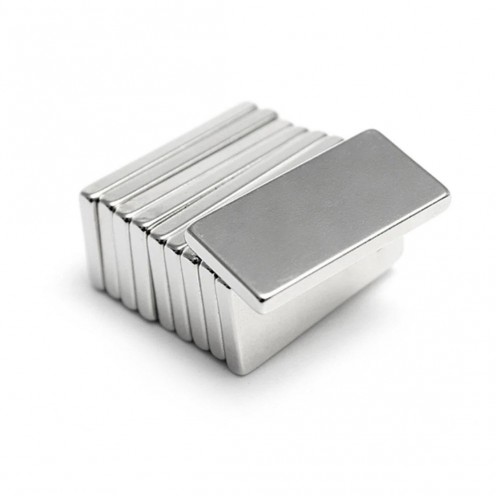
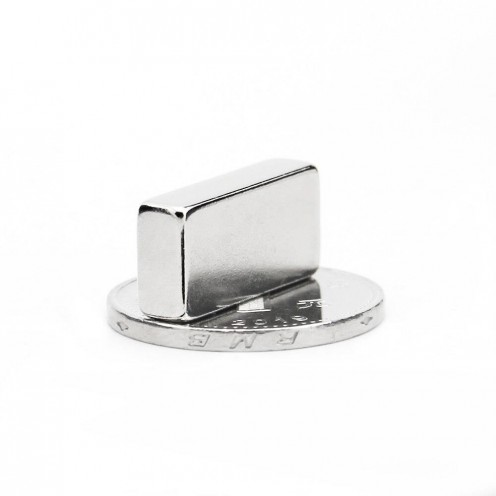
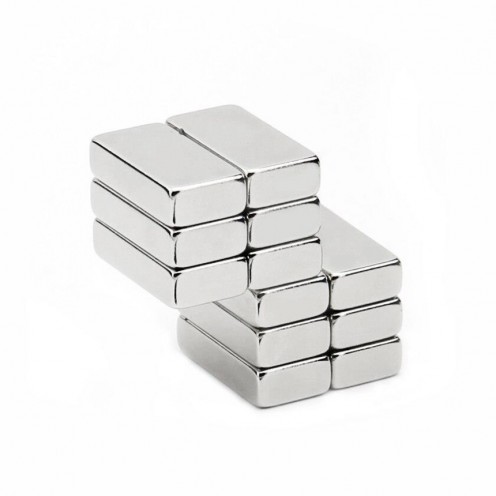
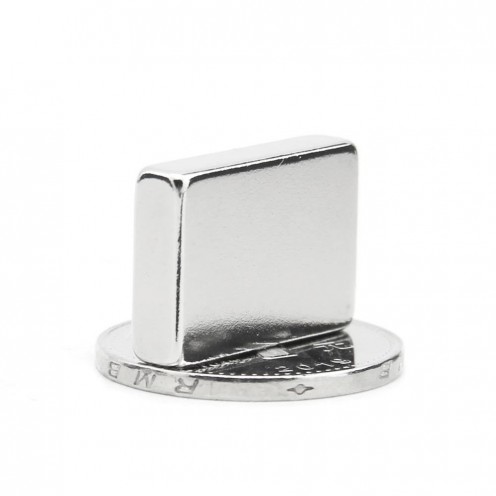
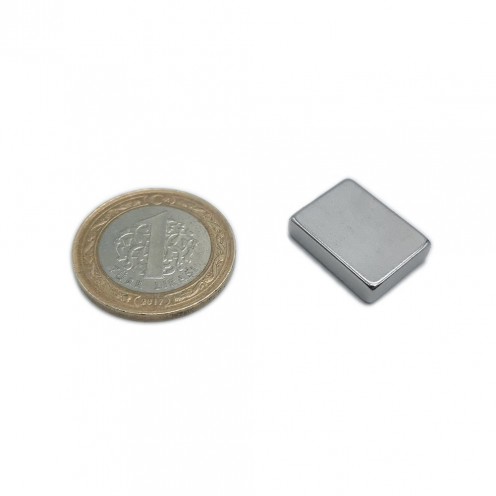
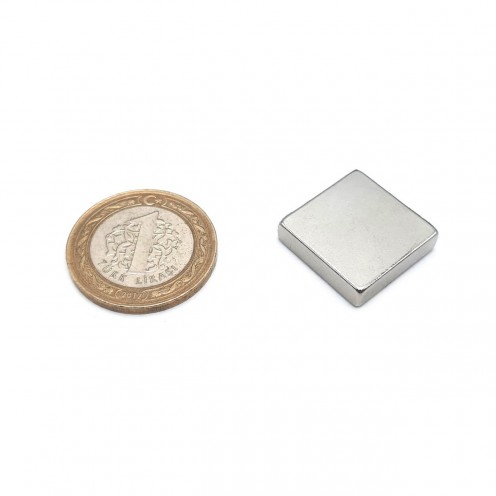
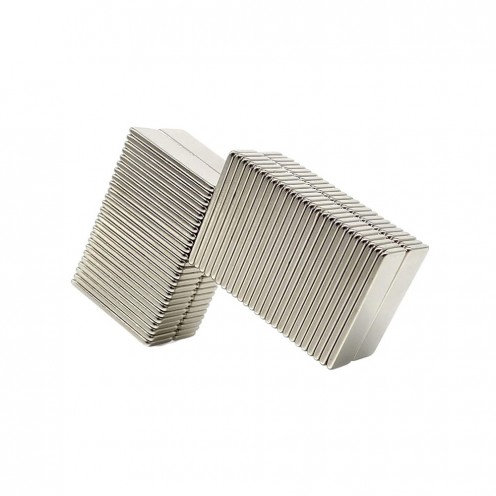
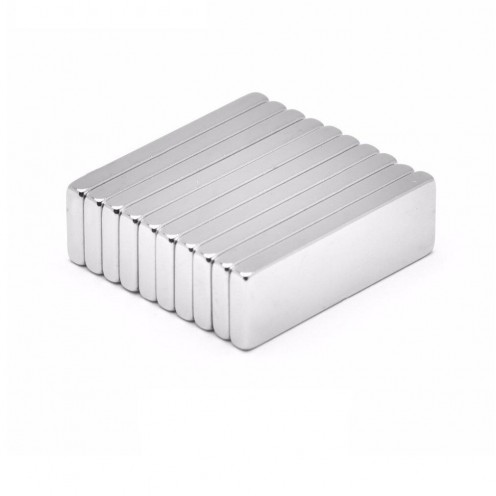
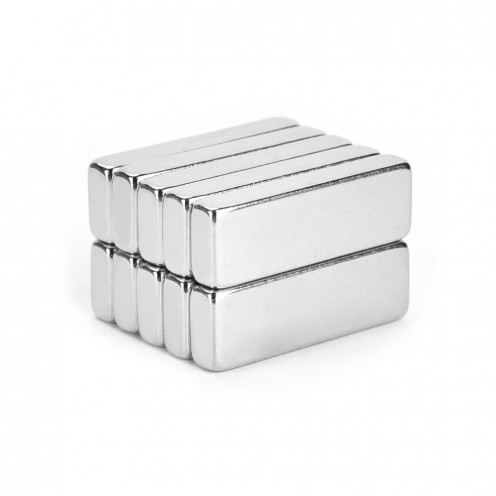
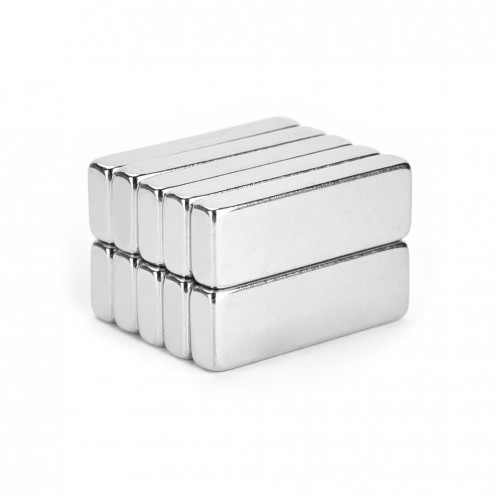
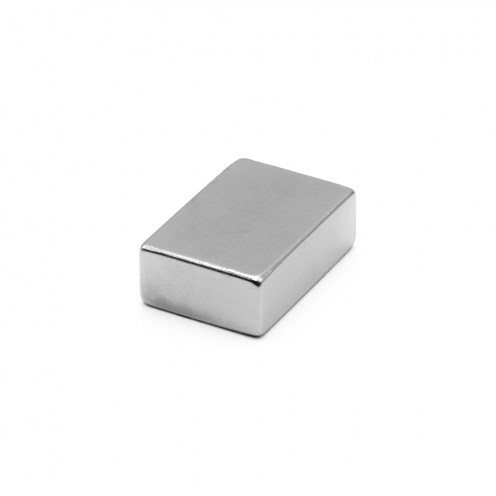
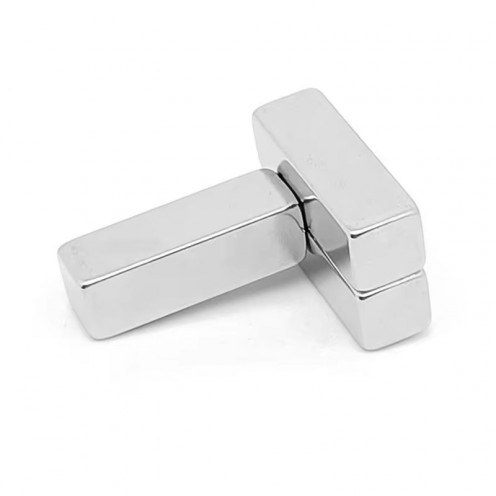
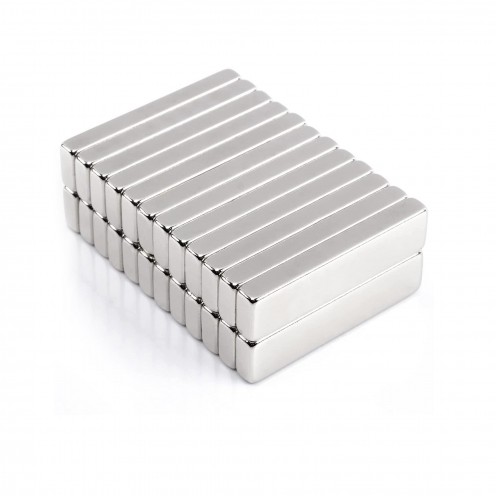
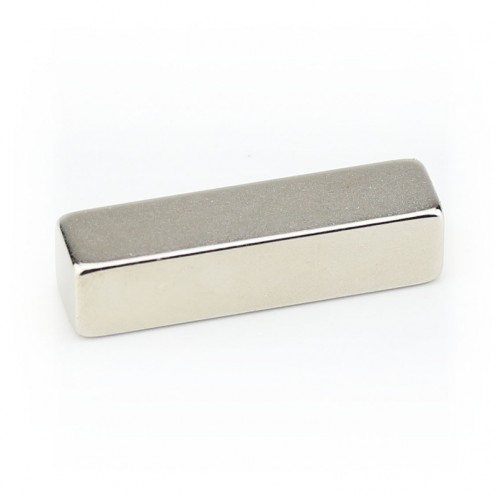
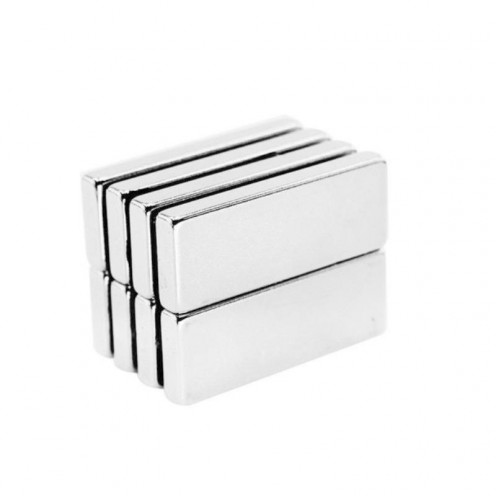
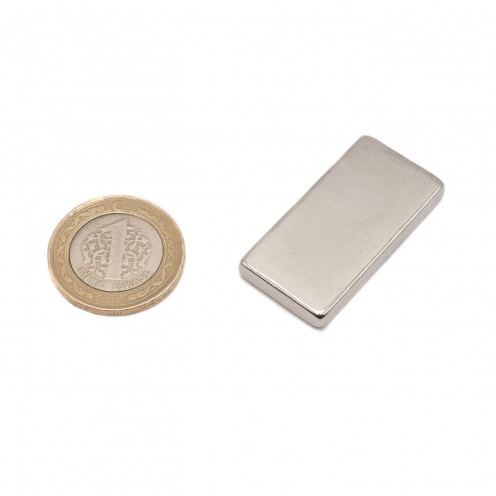
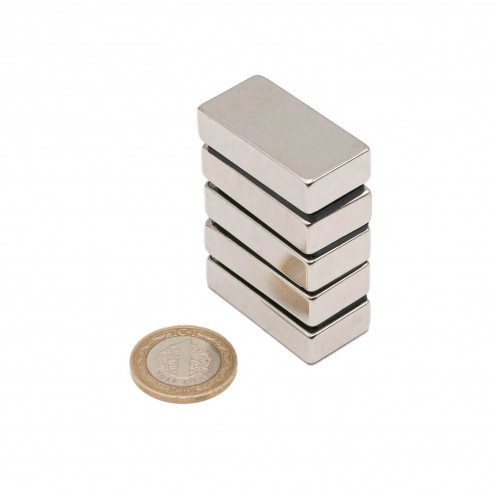
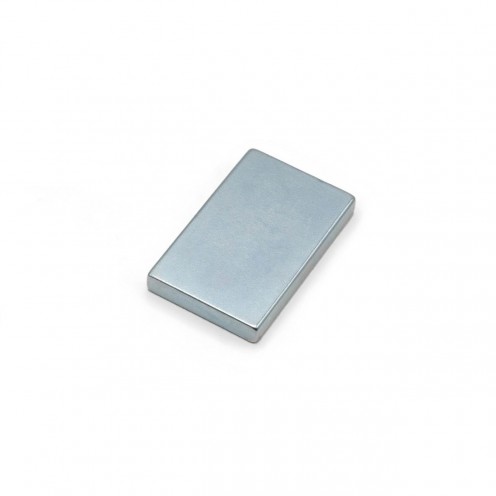
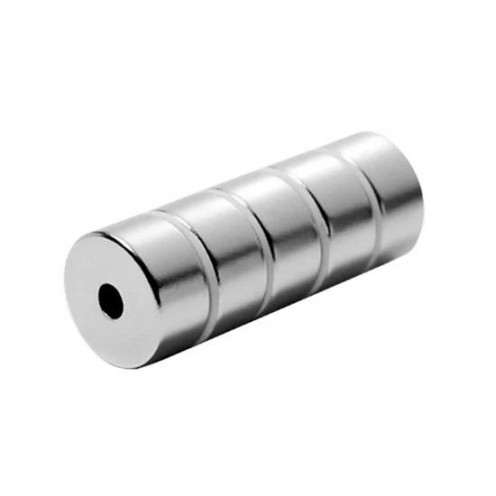
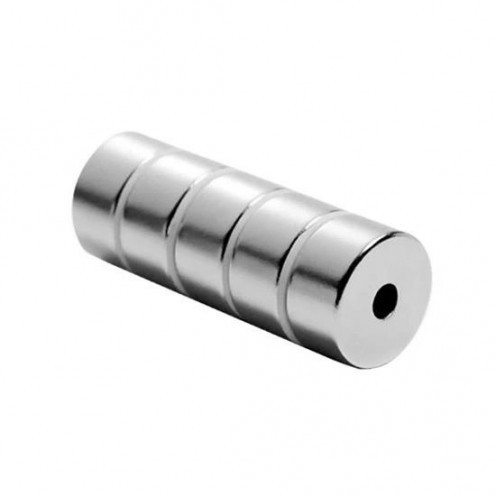
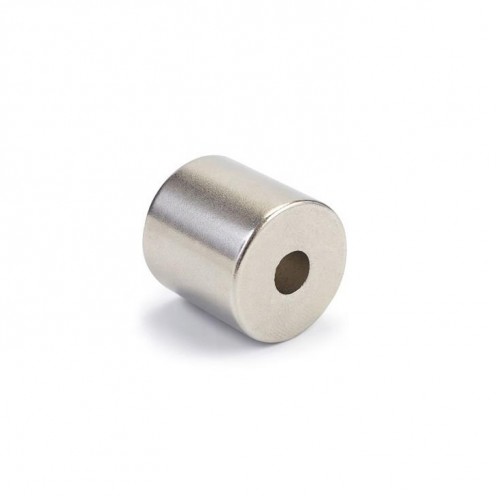
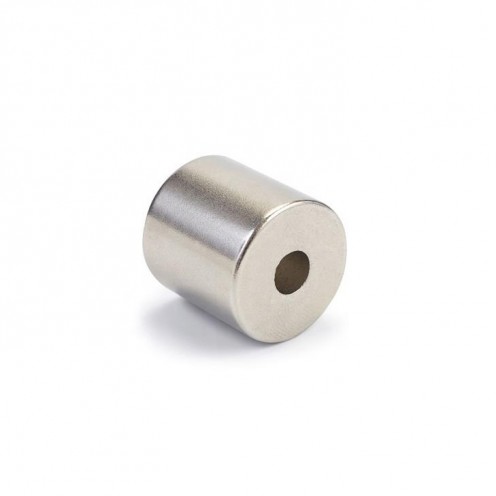
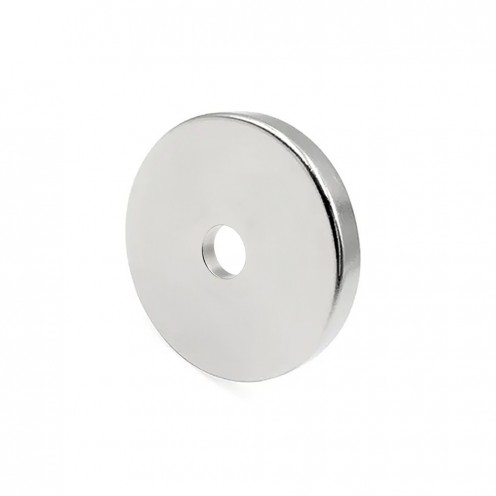
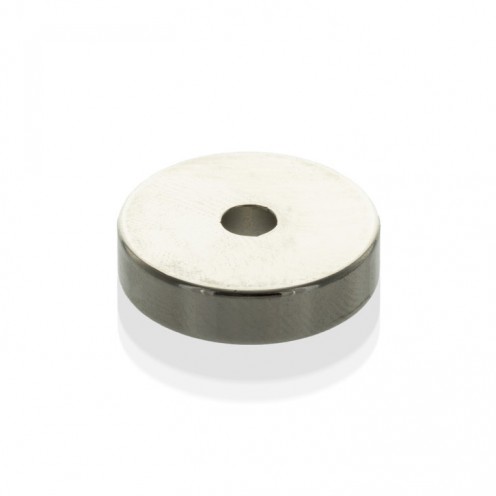
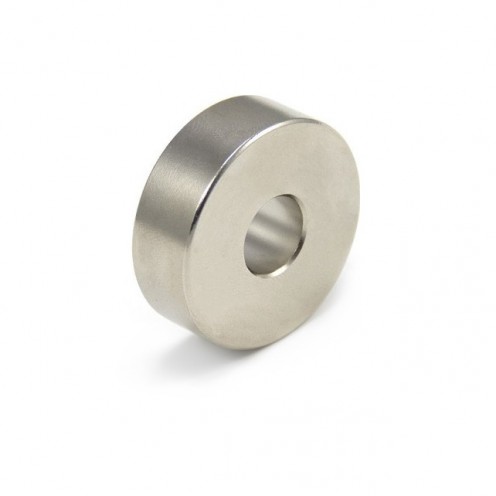
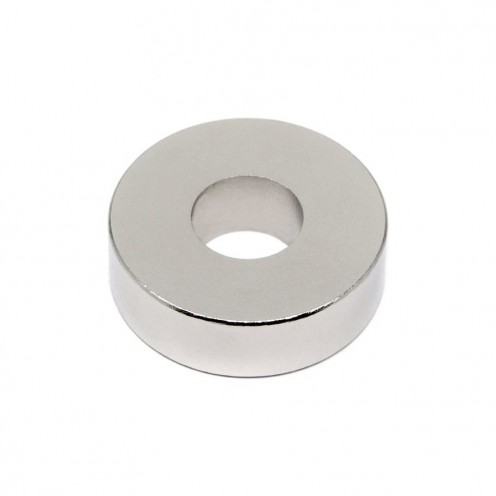
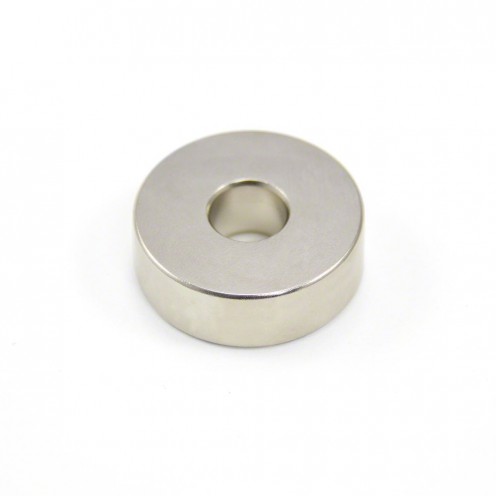
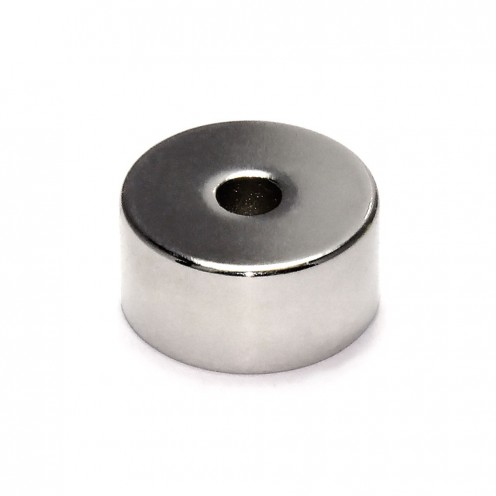
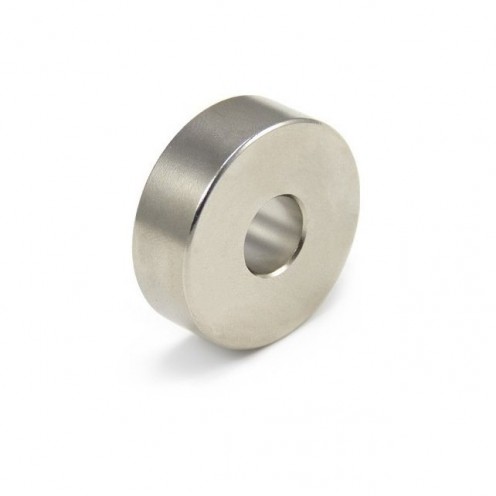
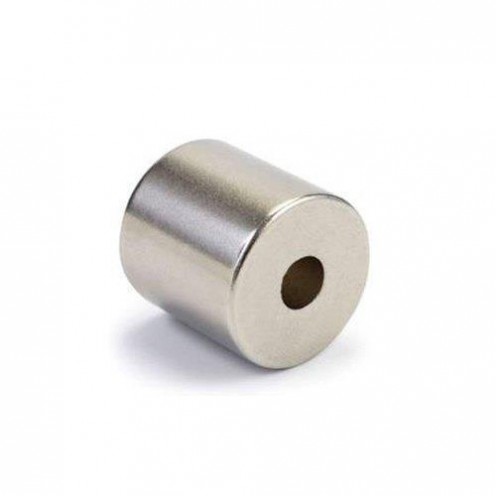
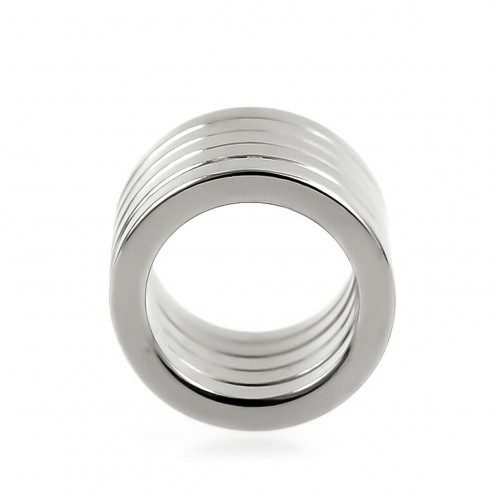
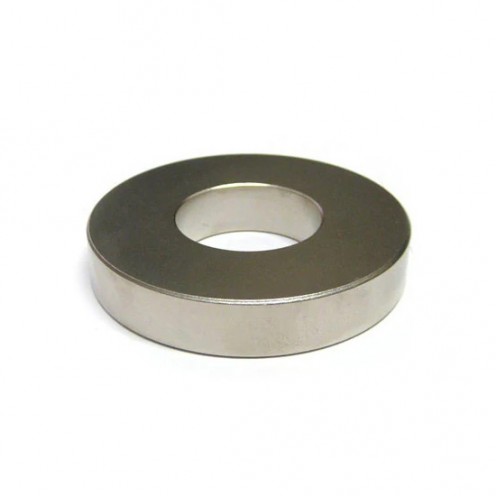
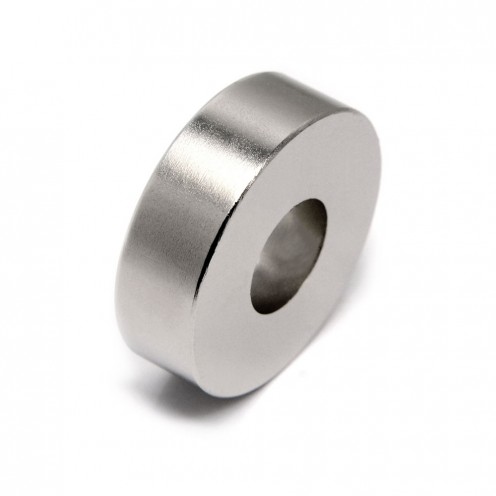
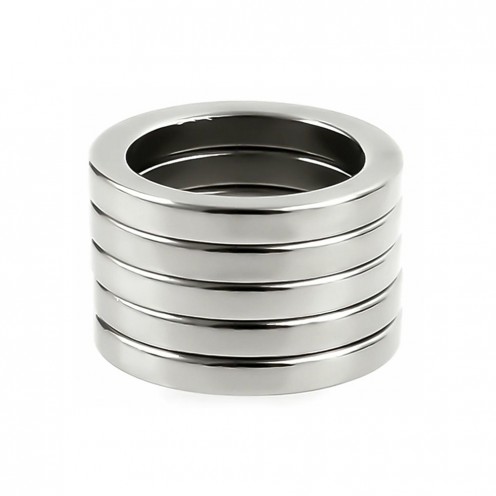
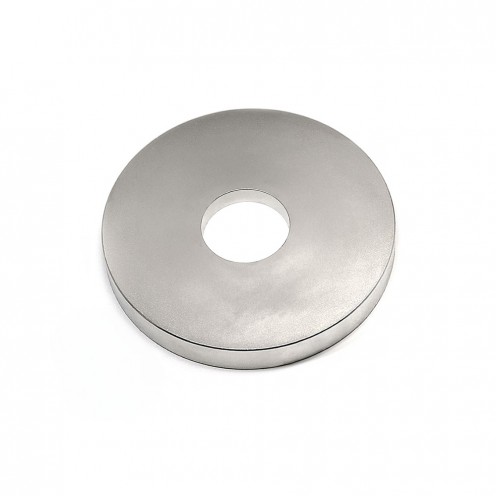
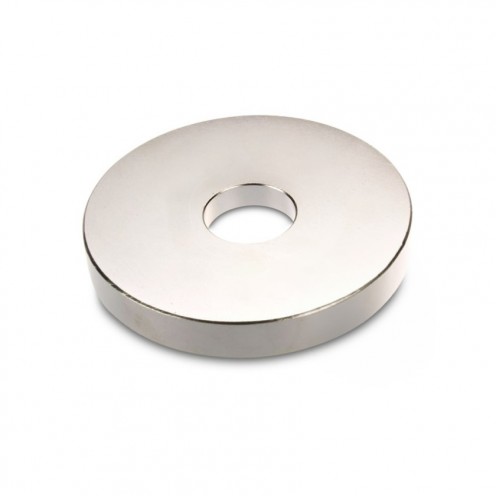
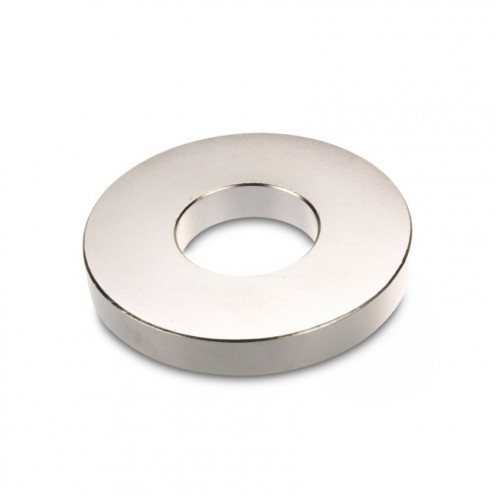
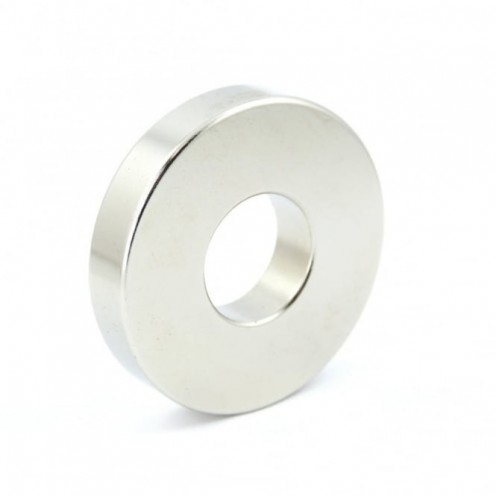
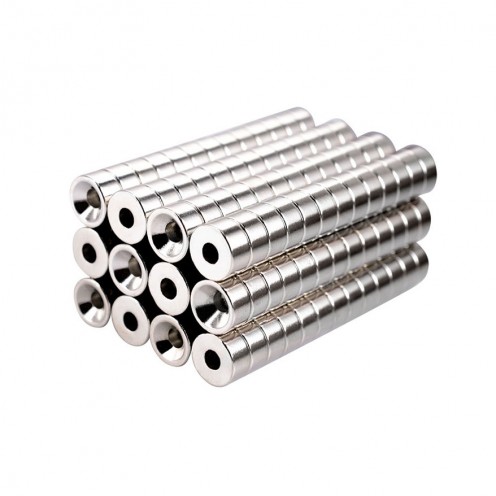
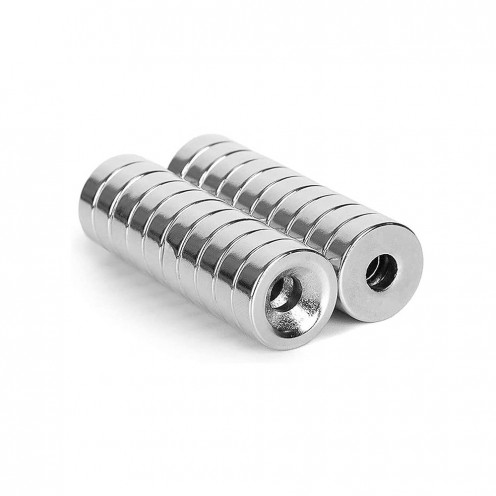
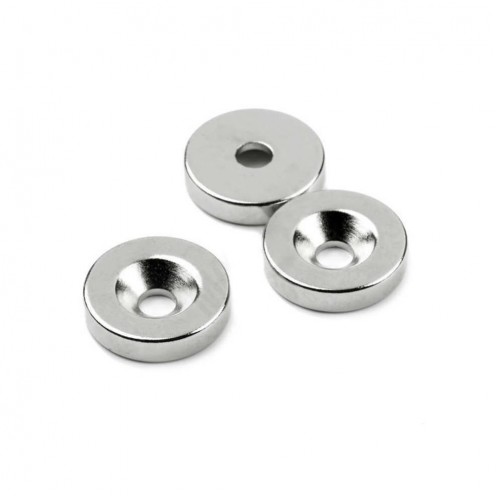
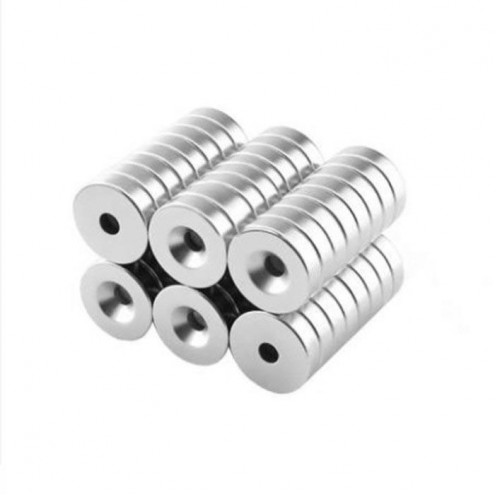
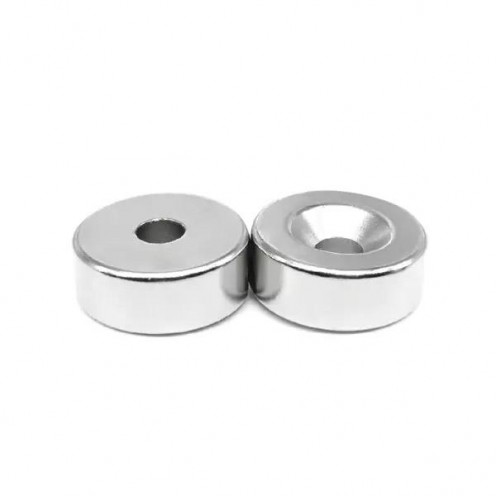
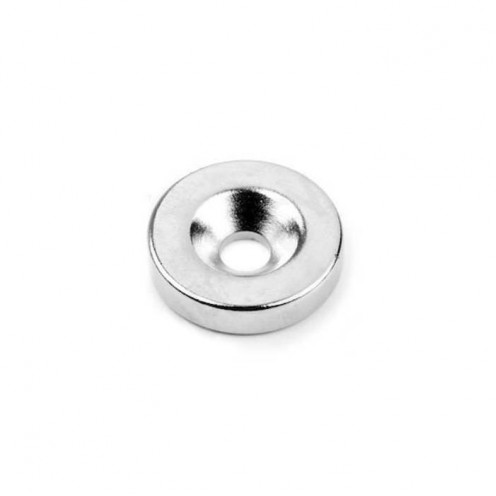
Magnet Types
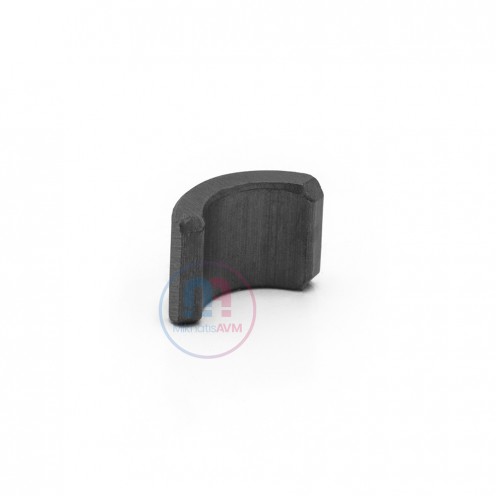
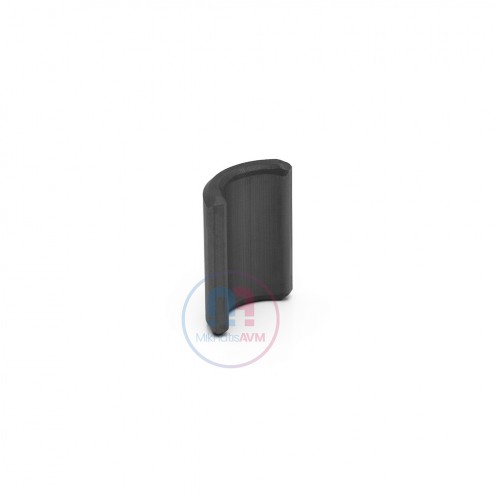
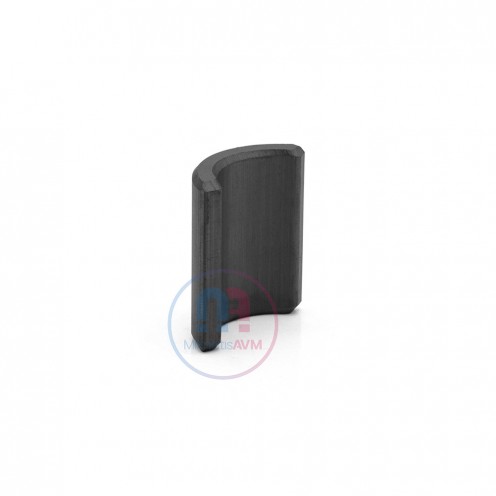
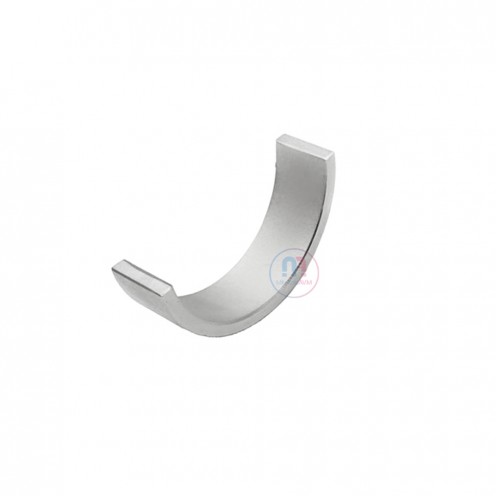
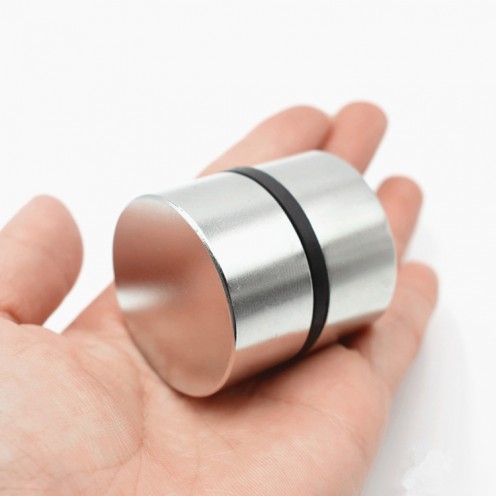
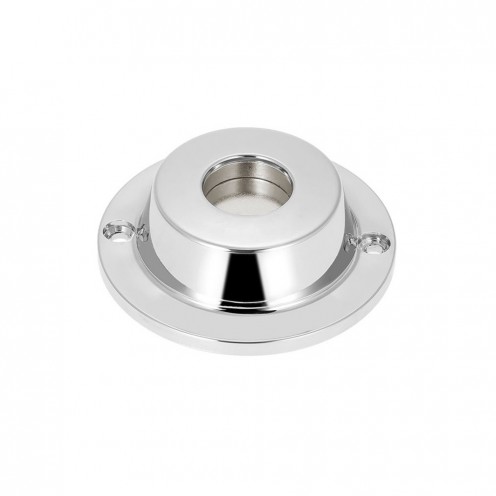
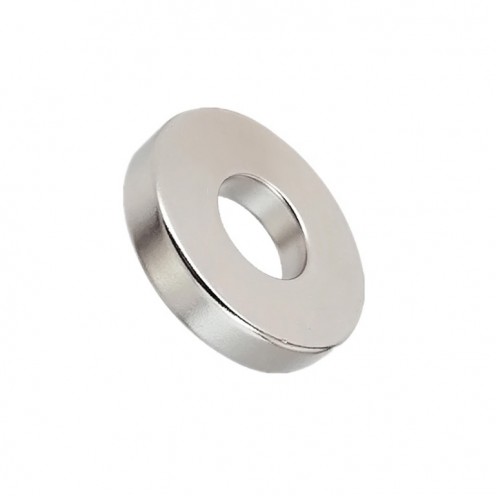
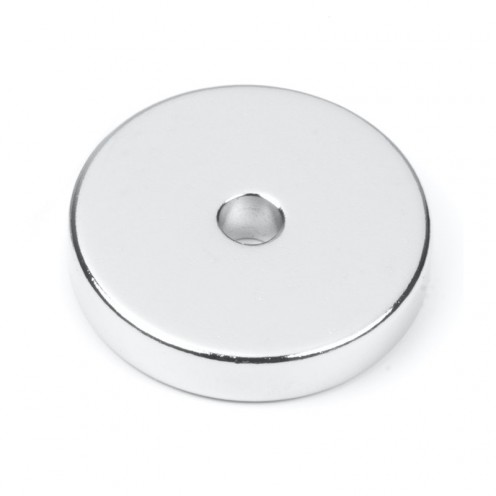
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)
Ferrite arc magnet is made by mixing metals such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc in small proportions. This ceramic material containing large proportions of iron oxide is used as ferrite motor magnet. Arc magnets have various dimensions su..
129.00 TL
Ex Tax:107.50 TL
- 10 Adet 109.65 TL
- 50 Adet 96.75 TL
- 250 Adet 83.85 TL
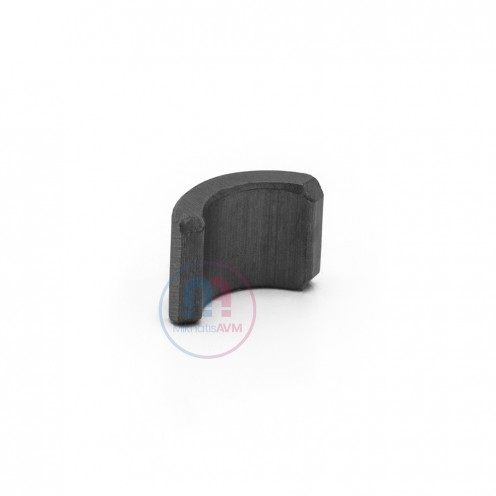
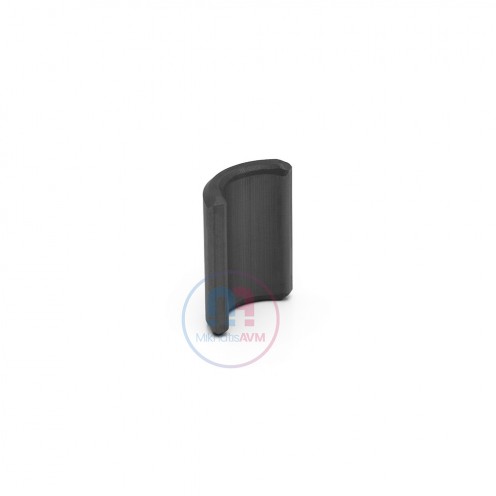
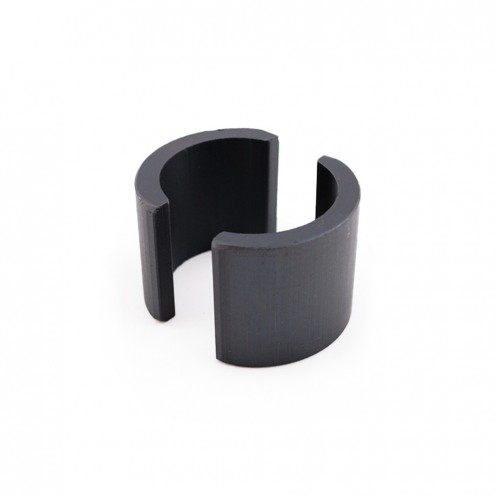
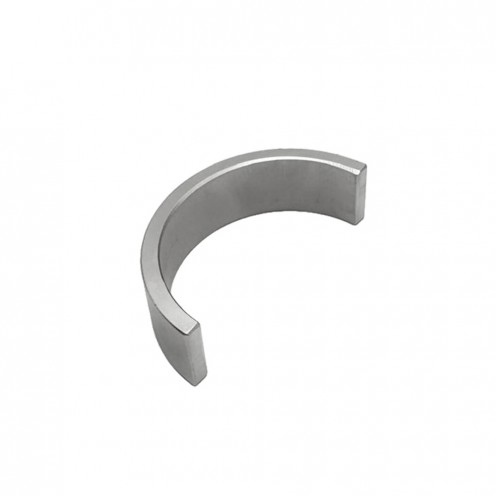
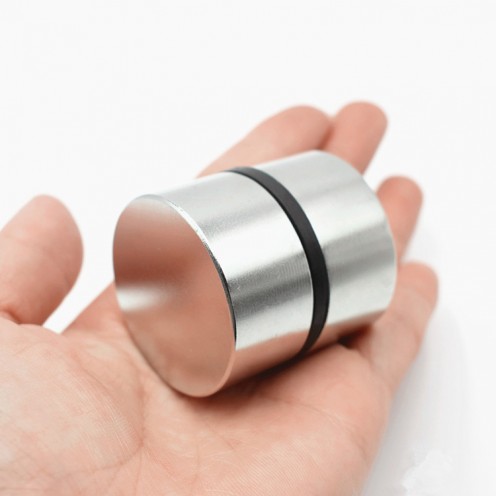
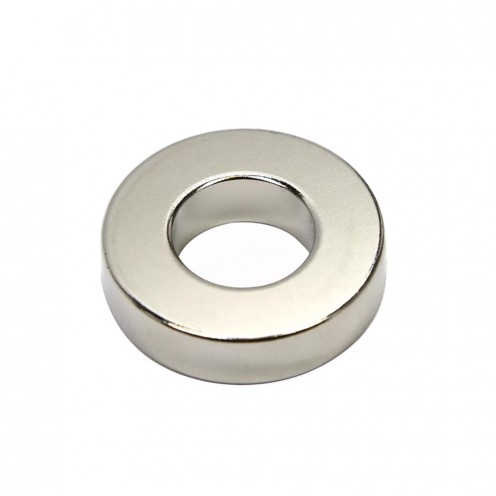
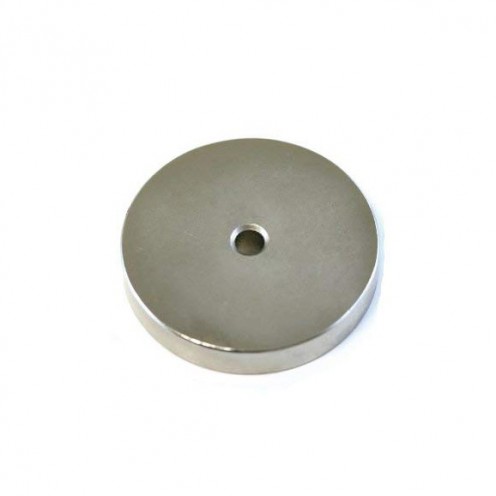
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
129.00 TL
Ex Tax:107.50 TL
- 10 Adet 109.65 TL
- 50 Adet 96.75 TL
- 250 Adet 83.85 TL
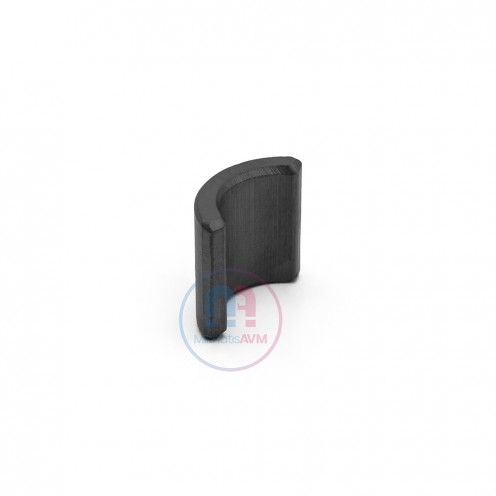
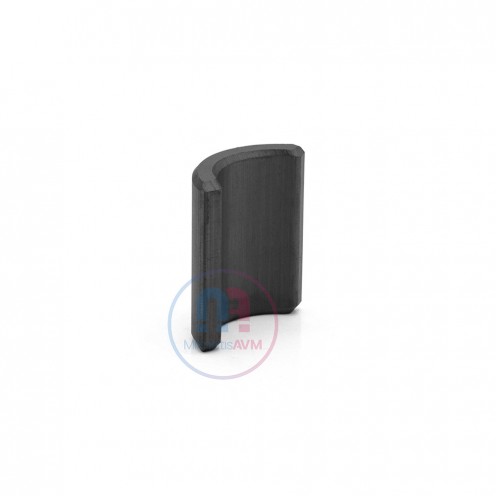
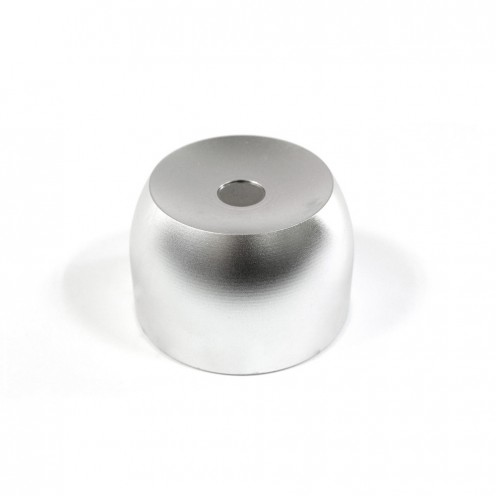
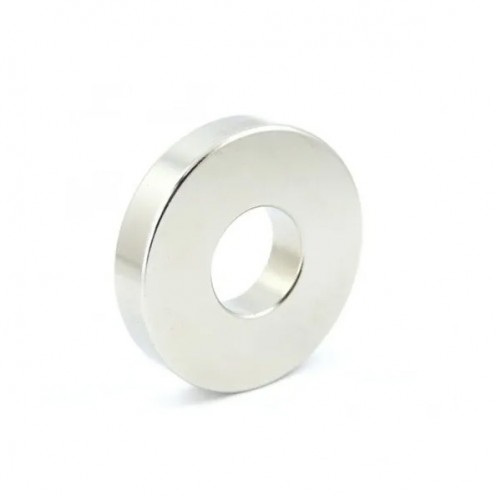
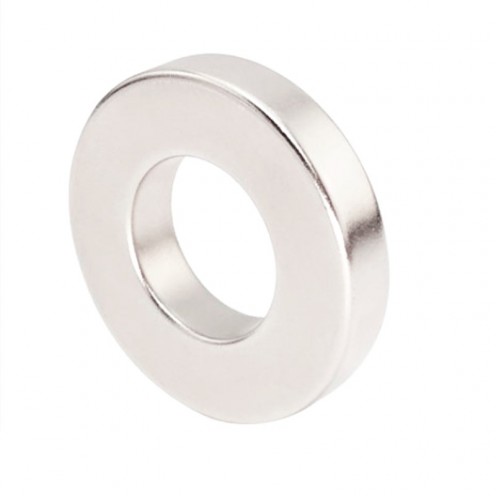
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)
Ferrite arc magnet is obtained by mixing various metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc in small proportions. A ceramic material is produced using iron oxide as the main ingredient. These arc magnets used as ferrite motor m..
135.00 TL
Ex Tax:112.50 TL
- 10 Adet 114.75 TL
- 50 Adet 101.25 TL
- 250 Adet 87.75 TL
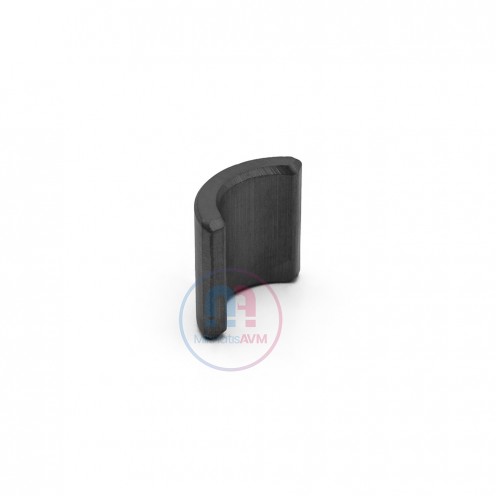
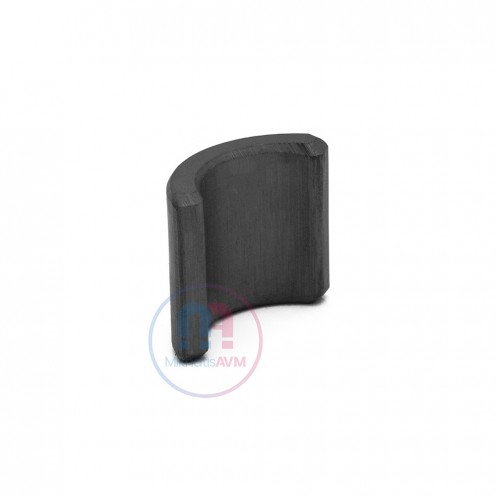
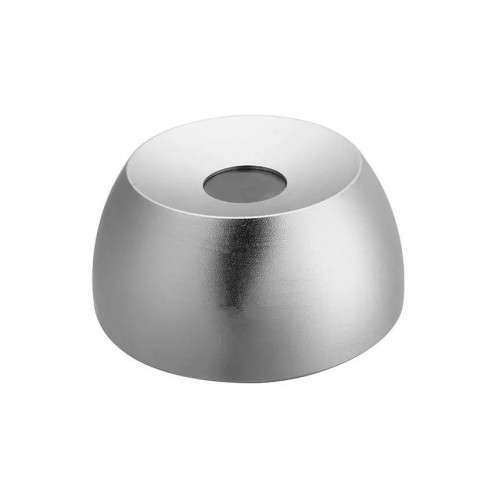
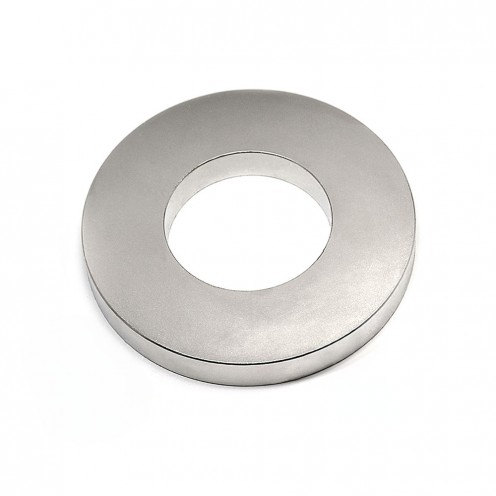
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
135.00 TL
Ex Tax:112.50 TL
- 10 Adet 114.75 TL
- 50 Adet 101.25 TL
- 250 Adet 87.75 TL
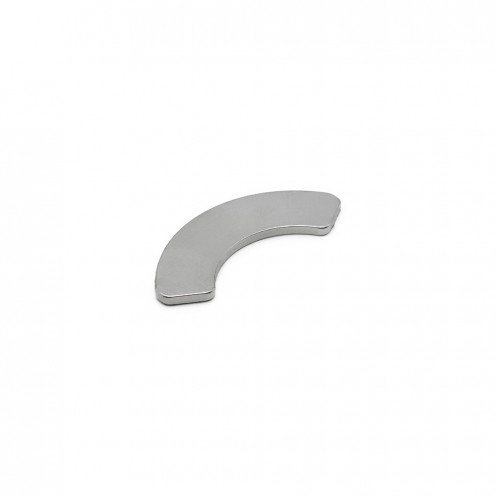
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole N)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion of iron (..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole N)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion of iron (..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)
Ferrite arc magnets are made by mixing metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc in specific proportions. A ceramic material is produced using iron oxide as the main component. These magnets are generally used in motor applica..
139.00 TL
Ex Tax:115.83 TL
- 10 Adet 118.15 TL
- 50 Adet 104.25 TL
- 250 Adet 90.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
139.00 TL
Ex Tax:115.83 TL
- 10 Adet 118.15 TL
- 50 Adet 104.25 TL
- 250 Adet 90.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole N)
Ferrite arc magnet is made with ferrite, a ceramic material consisting of a mixture of iron oxide and various metallic elements. These magnets have various dimensions such as inner diameter, outer diameter, thickness, width, length, par..
144.00 TL
Ex Tax:120.00 TL
- 10 Adet 122.40 TL
- 50 Adet 108.00 TL
- 250 Adet 93.60 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
144.00 TL
Ex Tax:120.00 TL
- 10 Adet 122.40 TL
- 50 Adet 108.00 TL
- 250 Adet 93.60 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)
A ferrite arc magnet is a mixture of ferrite, a ceramic material, with iron oxide and various metallic elements. These magnets are generally used in motor applications. These arc magnets used as ferrite motor magnets have various dimensions such as inner d..
149.00 TL
Ex Tax:124.17 TL
- 10 Adet 126.65 TL
- 50 Adet 111.75 TL
- 250 Adet 96.85 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
149.00 TL
Ex Tax:124.17 TL
- 10 Adet 126.65 TL
- 50 Adet 111.75 TL
- 250 Adet 96.85 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)A ferrite arc magnet is made by mixing small proportions of metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc with large proportions of ingredients such as iron (III) oxide. This mixture is fired into a ceramic material.Ferrite motor ma..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece) Summary:Ferrite arc magnet is obtained by mixing various metallic elements in small proportions and contains a large proportion of iron (III) oxide. As a ceramic material, these magnets are used in many areas such as motors.These magnets come in many differ..
164.00 TL
Ex Tax:136.67 TL
- 10 Adet 139.40 TL
- 50 Adet 123.00 TL
- 250 Adet 106.60 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
159.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 10 Adet 135.15 TL
- 50 Adet 119.25 TL
- 250 Adet 103.35 TL
..
179.00 TL
Ex Tax:149.17 TL
- 10 Adet 152.15 TL
- 50 Adet 134.25 TL
- 250 Adet 116.35 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)
Ferrite arc magnet is obtained by mixing various metallic elements in small proportions and contains large proportions of iron oxide. These magnets, which are a ceramic material, have different dimensions for use in motors, including inner diameter, outer ..
169.00 TL
Ex Tax:140.83 TL
- 10 Adet 143.65 TL
- 50 Adet 126.75 TL
- 250 Adet 109.85 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece - Outer Pole S - South)Ferrite arc magnets are produced by combining small proportions of additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. Essentially, they are made using a ceramic material containing a large proportion o..
169.00 TL
Ex Tax:140.83 TL
- 10 Adet 143.65 TL
- 50 Adet 126.75 TL
- 250 Adet 109.85 TL
Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece)
A ferrite arc magnet consists of a mixture of various metallic elements and iron oxide to produce a ceramic material. These magnets are generally used in motor applications and have various dimensions such as inner diameter, outer diameter, thickness, widt..
179.00 TL
Ex Tax:149.17 TL
- 10 Adet 152.15 TL
- 50 Adet 134.25 TL
- 250 Adet 116.35 TL
Y35 Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece Price)Ferrite arc magnet is made by mixing metals such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc in small proportions. It is a ceramic material containing a large proportion of iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3, rust) and made by firing.This Y35 grade ..
Teklif İsteyin
- 500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 10000 Adet 0.00 TL
Y35 Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece Price)Ferrite arc magnet is made by mixing small proportions of one or more additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc. It contains large proportions of iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3, rust), which is mixed and fired into..
36%
159.00 TL 249.00 TL
Ex Tax:132.50 TL
- 5 Adet 224.10 TL
- 25 Adet 199.20 TL
- 100 Adet 174.30 TL
Y35 Ferrite Arc Magnet, Motor Magnet (1 Piece Price)A ferrite arc magnet is made by mixing small proportions of one or more additional metallic elements such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel and zinc. In terms of content, it is a ceramic material made by mixing and firing large proportions of..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
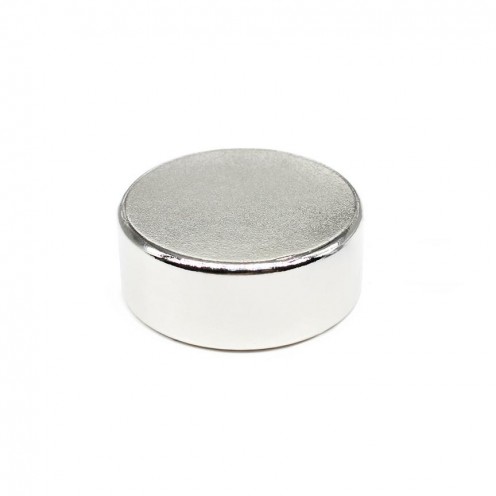
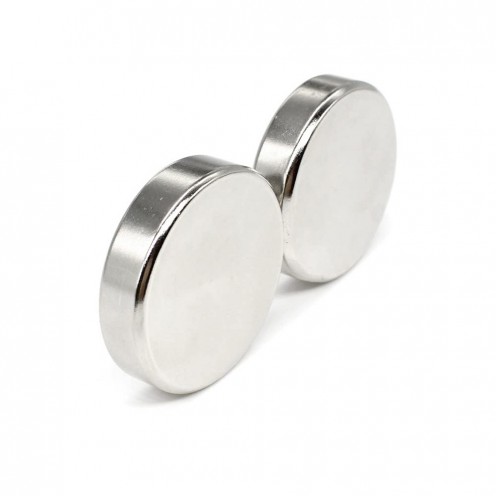
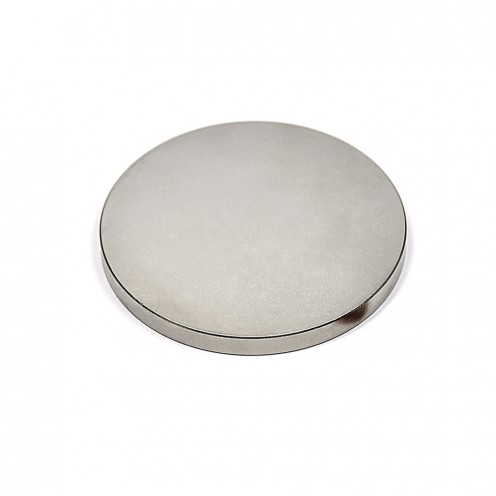
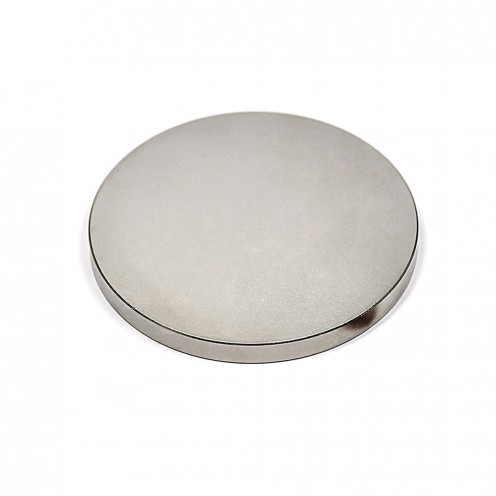
17.5x4 mm Strong Neodymium Disc Magnet – N45 Grade
With a diameter of 17.5 mm and a thickness of 4 mm, this neodymium disc magnet stands out for its permanent magnetic power. Featuring N45 grade strength, it ranks among the most powerful magnetic materials on Earth. Thanks to its compact structur..
35.00 TL
Ex Tax:29.17 TL
Arc (Motor) Magnet – Powerful and Efficient Magnetic Performance
The Arc magnet is a powerful magnet designed specifically for electric motors, generators, magnetic couplings, and sensors. Its curved form ensures perfect compatibility with rotating systems, helping to direct the magnetic field in t..
Teklif İsteyin
Arc (Motor) Magnet – Powerful and Efficient Magnetic Performance
The Arc magnet is a powerful magnet designed specifically for electric motors, generators, magnetic couplings, and sensors. Its curved form ensures perfect compatibility with rotating systems, helping to direct the magnetic field in t..
Teklif İsteyin
1x1 mm Special Neodymium Magnet
The 1 mm diameter neodymium magnet is designed exclusively for special projects with its ultra-compact size. With a thickness of 1 mm, it can be mounted in the smallest spaces. The product is nickel-plated and N35 grade quality. The 1 mm diameter nickel-plated neodym..
1.20 TL
Ex Tax:1.00 TL
- 500 Adet 1.06 TL
- 2500 Adet 0.96 TL
- 10000 Adet 0.84 TL
Mini Neo Magnet - 2x1 mm
This mini neodymium magnet, with a diameter of 2 mm and thickness of 1 mm, is specifically designed for special projects. The product is nickel-plated and N35 grade quality. Compared to zinc-coated versions, these nickel-plated neodymium magnets offer superior strength and ..
2.00 TL
Ex Tax:1.67 TL
- 500 Adet 1.76 TL
- 2500 Adet 1.60 TL
- 10000 Adet 1.40 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - 2x2 mm
This small neodymium magnet, with a diameter of 2 mm and thickness of 2 mm, is specially designed for precision projects. The product features nickel plating and N35 grade quality. Compared to zinc-coated alternatives, these nickel-plated neodymium magnets offer supe..
2.50 TL
Ex Tax:2.08 TL
- 500 Adet 2.20 TL
- 2500 Adet 2.00 TL
- 10000 Adet 1.75 TL
Ø2x2 mm N35 Neodymium Sensor Magnet - Reed Switch On/Off Magnet (2 Pieces)
The product is used in pairs and 2 pieces will be sent to you. The price is for 2 pieces. This type of sensor magnet is used in industries such as automotive, electrical, electronics, and defense. Through this neodymium sens..
32.00 TL
Ex Tax:26.67 TL
- 100 Adet 25.60 TL
- 500 Adet 23.04 TL
- 2500 Adet 20.80 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 3 mm
Thickness: 1.5 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Strength: 0-100 g
Coating: Nickel/Zinc
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Grade: N35
Certification and Manufacturing Details
Our magnets come with Gauss certification, available upon reques..
3.00 TL
Ex Tax:2.50 TL
- 500 Adet 2.64 TL
- 2500 Adet 2.40 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.10 TL
3mm Diameter, 2mm Thickness Round Neodymium Magnet N35
This cylindrical neodymium magnet, measuring D3x2 mm, features nickel plating for enhanced magnetic strength. Despite its compact size of 3mm diameter and 2mm thickness, this neodymium magnet demonstrates remarkable pulling force.
Usage and ..
3.40 TL
Ex Tax:2.83 TL
- 500 Adet 2.99 TL
- 2500 Adet 2.72 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.38 TL
Neodymium Cylindrical Magnet - 3mm Diameter, 3mm Thickness
This cylindrical neodymium magnet has found its place in special projects due to its compact size and strength. It's perfect for your projects, assignments, and use in homes and schools. The product features nickel plating and is N35 grade ..
3.80 TL
Ex Tax:3.17 TL
- 500 Adet 3.34 TL
- 2500 Adet 3.04 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.66 TL
Neodymium Cylindrical Magnet - 3x6 mm
This N35 neodymium cylindrical magnet, measuring 3mm in diameter and 6mm in thickness, is perfect for hobby experiments, educational purposes, and office use. It's also suitable for use as a sensor magnet. The magnet features nickel plating for enhanced corrosi..
4.20 TL
Ex Tax:3.50 TL
- 500 Adet 3.70 TL
- 2500 Adet 3.36 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.94 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D4x2 mm
This N35 neodymium magnet is versatile enough for hobby experiments, educational purposes, and office use. As a super-strong neodymium magnet, it's suitable for both hobby applications and professional projects.
With its 4mm length, this compact neodymium magnet ..
4.40 TL
Ex Tax:3.67 TL
- 500 Adet 3.87 TL
- 2500 Adet 3.52 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.08 TL
D4x4 mm Round Small Neodymium Magnet N35
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron), these magnets offer incredible strength despite their compact size. They're widely used in various applications, from..
4.80 TL
Ex Tax:4.00 TL
- 500 Adet 4.22 TL
- 2500 Adet 3.84 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.36 TL
D4x6 mm Round Cylindrical Neodymium Magnet N35
Despite its compact 4mm diameter, this neodymium magnet demonstrates remarkable strength. As nature's strongest permanent magnet, it maintains its magnetic properties over extended periods. This small yet powerful magnet is versatile enough for hobby u..
5.20 TL
Ex Tax:4.33 TL
- 500 Adet 4.58 TL
- 2500 Adet 4.16 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.64 TL
Neodymium Round Disc Magnet - 5mm Diameter, 1mm Thickness
This circular neodymium disc magnet is versatile enough for projects, home use, and office applications. Students can safely use it for school experiments. As an N35 grade magnet, it features a durable coating that won't peel or tarnish. Thi..
5.20 TL
Ex Tax:4.33 TL
- 500 Adet 4.58 TL
- 2500 Adet 4.16 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.64 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 5 mm
Thickness: 1.5 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Pull Force: 0-1 kg
Coating: Nickel
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Grade: N35
Quality Certification and Manufacturing
Our magnets are supplied with Gauss certification, available upon re..
5.40 TL
Ex Tax:4.50 TL
- 500 Adet 4.75 TL
- 2500 Adet 4.32 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.78 TL
Neodymium Round Disc Magnet - 5mm Diameter, 2mm Thickness
The neodymium disc magnet has a round structure and can be used in projects, homes, and offices. Students can easily use it in experiments at schools. Our magnet is N35 quality, its coating doesn't peel off or tarnish. Additionally, this mag..
5.80 TL
Ex Tax:4.83 TL
- 500 Adet 5.10 TL
- 2500 Adet 4.64 TL
- 10000 Adet 4.06 TL
5x3 mm Cylindrical Neodymium Magnet N35
A small magnet with 5 mm diameter and 3 mm thickness (5mmx3mm). These neodymium magnets, being the strongest magnets in nature, maintain their strength for extended periods. This small magnet with high magnetic pull can be used in homes as a hobby, schools, a..
6.00 TL
Ex Tax:5.00 TL
- 50 Adet 5.40 TL
- 250 Adet 4.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.20 TL
Diameter 5 mm, Thickness 4 mm Round Neodymium Magnet N35This neodymium magnet, also known as a cylinder magnet, is 5 mm in diameter and 4 mm thick. Its strength is increased with nickel plating. Despite its small size, its attraction power is quite good.Instructions for Use:Detachment: Separate by p..
6.20 TL
Ex Tax:5.17 TL
- 50 Adet 5.58 TL
- 250 Adet 4.96 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.34 TL
D5x5 mm Round Small Neodymium Magnet N35
Despite its small size, the 5 mm diameter neodymium magnet stands out with its powerful structure. These neodymium magnets, being the strongest magnets found in nature, retain their strength for extended periods. This small magnet with high magnetic attracti..
6.80 TL
Ex Tax:5.67 TL
- 50 Adet 6.12 TL
- 250 Adet 5.44 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.76 TL
D5x10 mm Round Small Neodymium Magnet N35Neodymium magnets are resistant to temperatures up to 80°C. This 5x10 mm neodymium magnet has a cylindrical structure and maintains the same strength for many years. It has a 10 mm thickness and can be used in special hobbies. The product is of N35 quality an..
10.00 TL
Ex Tax:8.33 TL
- 50 Adet 9.00 TL
- 250 Adet 8.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.00 TL
D5x15 mm Round Small Neodymium Magnet N35This 5mm diameter neodymium magnet is cylindrical and 15mm long. It can be used in special hobbies, various projects, schools and experiments. Neodymium, the strongest magnet in nature, retains its strength for a long time. This magnet is durable and protecte..
15.36 TL
Ex Tax:12.80 TL
- 50 Adet 13.82 TL
- 250 Adet 12.29 TL
- 1000 Adet 10.75 TL
5x25 mm Neodymium Cylinder Magnet
The 5 mm diameter neodymium magnet is a cylindrical permanent magnet. Neodymium magnets, among the strongest magnets on Earth, are specially processed into a cylindrical structure. This 25 mm thick magnet is designed for your hobby and special projects.
Nickel-p..
23.60 TL
Ex Tax:19.67 TL
- 50 Adet 21.24 TL
- 250 Adet 18.88 TL
- 1000 Adet 16.52 TL
D6x1 mm Round Neodymium Magnet N35
The neodymium magnet, also known as a cylinder magnet, D6x1 mm has been nickel-plated to enhance its strength. This neodymium magnet with a 6 mm diameter has a thickness of 1 mm. Despite its small size, it offers excellent magnetic attraction.
When removing the..
6.20 TL
Ex Tax:5.17 TL
- 50 Adet 5.58 TL
- 250 Adet 4.96 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.34 TL
D6x1.5 mm Round Neodymium Magnet N35This neodymium magnet, also known as a cylinder magnet, is 6 mm in diameter and 1.5 mm thick. Its strength is increased with nickel plating. Despite its small size, its attraction power is quite good.Instructions for Use:Detachment: Separate from the adhesive by p..
6.40 TL
Ex Tax:5.33 TL
- 50 Adet 5.76 TL
- 250 Adet 5.12 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.48 TL
Neodymium Round Disc Magnet - 6 mm Diameter, 2 mm ThicknessThis neodymium disk magnet has a diameter of 6 mm and a thickness of 2 mm. With its round structure, it can be used in projects, homes and offices. This magnet, which students can easily use in experiments in schools, is N35 quality and main..
6.80 TL
Ex Tax:5.67 TL
- 50 Adet 6.12 TL
- 250 Adet 5.44 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.76 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D6x3 mm
N35 neodymium round magnet can be used in hobby experiments, schools, and offices. This super-strong neodymium magnet can be preferred for hobby purposes as well as in various projects.
The small neodymium magnet offers high magnetic attraction with its 4 mm leng..
7.40 TL
Ex Tax:6.17 TL
- 50 Adet 6.66 TL
- 250 Adet 5.92 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.18 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D6x4 mmThe N35 neodymium round magnet can be used in hobby experiments, schools and offices. This super strong neodymium magnet is also ideal for hobby projects and various other projects.Specifications:Size: 6 mm diameter, 4 mm lengthQuality: N35Areas of Use: Hobby projects..
7.80 TL
Ex Tax:6.50 TL
- 50 Adet 7.02 TL
- 250 Adet 6.24 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.46 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D6x5 mm
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, neodymium magnets offer incredible strength despite their ti..
8.00 TL
Ex Tax:6.67 TL
- 50 Adet 7.20 TL
- 250 Adet 6.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.60 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D6x6 mm
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements), they rank among the strongest permanent magnets available. Despite their compact size, they deliver remarkable ma..
9.00 TL
Ex Tax:7.50 TL
- 50 Adet 8.10 TL
- 250 Adet 7.20 TL
- 1000 Adet 6.30 TL
Neodymium Cylinder Magnet - 6 mm Diameter, 10 mm Thickness
This cylindrical neodymium magnet has an average pulling force of 5 kg. You can easily use it in your projects, homework, homes, and schools. The product is nickel-plated and of N35 quality. Nickel-plated products are stronger and more resi..
14.50 TL
Ex Tax:12.08 TL
- 50 Adet 13.05 TL
- 250 Adet 11.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 10.15 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D6x25 mm
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). As one of the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power despite their small size. These m..
25.00 TL
Ex Tax:20.83 TL
- 50 Adet 22.50 TL
- 250 Adet 20.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 17.50 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D7x1.5 mmDespite its small size, this N35 neodymium magnet offers high attraction and can be used in a variety of applications. It can be used safely in hobby experiments, schools and offices, as well as in your projects.Areas of Use:Hobbies and Experiments: Ideal for small ..
7.00 TL
Ex Tax:5.83 TL
- 50 Adet 6.30 TL
- 250 Adet 5.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.90 TL
7 mm Diameter, 2 mm Thickness Round Neodymium Magnet N35
The neodymium magnet, also known as a cylinder magnet, measuring 7x2 mm has been enhanced with nickel plating for increased strength. This neodymium magnet has a 7 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness. Despite its compact size, it offers excellent ..
7.50 TL
Ex Tax:6.25 TL
- 50 Adet 6.75 TL
- 250 Adet 6.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.25 TL
8x1 mm Neodymium Round Disc MagnetThese high-powered 8 mm x 1 mm neodymium disc magnets are ideal for hobby use. Use adhesive to mount them to a plastic or wooden surface, or insert them into an 8 mm diameter hole for special projects.Areas of UseHandicraftsSouvenirsOrnament MagnetsFurniture DesignK..
8.00 TL
Ex Tax:6.67 TL
- 50 Adet 7.20 TL
- 250 Adet 6.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.60 TL
Neodymium Round Disc Magnet - 8mm Diameter, 2mm Thickness
The neodymium disc magnet features a round structure and is suitable for use in projects, homes, and offices. Students can easily utilize it in school experiments. Our magnet is N35 quality grade, with a coating that won't peel or tarnish. F..
8.50 TL
Ex Tax:7.08 TL
- 50 Adet 7.65 TL
- 250 Adet 6.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.95 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 8 mm
Thickness: 3 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Strength: 0-3 kg
Coating: Nickel
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Quality: N35
Certification
Our magnets come with Gauss certification and can be provided to..
8.80 TL
Ex Tax:7.33 TL
- 50 Adet 7.92 TL
- 250 Adet 7.04 TL
- 1000 Adet 6.16 TL
8x4 mm Neodymium Magnet
This nickel-plated neodymium magnet, measuring 8 mm in diameter and 4 mm in thickness, is N35 grade and powerful. It can be used in hobby experiments, schools, and offices. While this super-strong neodymium magnet is perfect for hobby purposes, it's also suitable for profess..
9%
9.00 TL 10.00 TL
Ex Tax:7.50 TL
- 50 Adet 9.00 TL
- 250 Adet 8.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.00 TL
8 mm Diameter Round Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements), they rank among the strongest permanent magnets, delivering incredible power despite their small size. They are ..
16.00 TL
Ex Tax:13.33 TL
- 50 Adet 14.40 TL
- 250 Adet 12.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 11.20 TL
8x5 mm Neodymium Magnet
The N35 neodymium round magnet, measuring 8 mm in diameter and 5 mm in thickness, is suitable for hobby experiments, schools, and office use. While this super-strong neodymium magnet is ideal for hobby purposes, it can also be utilized in professional projects. For all your ..
10.62 TL
Ex Tax:8.85 TL
- 50 Adet 9.56 TL
- 250 Adet 8.50 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.43 TL
8x8 mm Neodymium Magnet N35 QualityThis 8 mm diameter and 8 mm long neodymium magnet is super strong. It is even stronger thanks to its nickel coating and can be used in your special projects. Preferred in schools and experiments, this neodymium magnet is one of the strongest magnets in nature and m..
14.40 TL
Ex Tax:12.00 TL
- 50 Adet 12.96 TL
- 250 Adet 11.52 TL
- 1000 Adet 10.08 TL
8x10 mm Strong Neodymium Cylindrical MagnetThis 8 mm diameter very strong neodymium magnet is nickel plated and impact resistant. It has a 10 mm long cylindrical structure. Neodymium permanent magnets offer a continuous magnetic field without the need for additional power. They offer 3-4 times highe..
18.88 TL
Ex Tax:15.73 TL
- 50 Adet 16.99 TL
- 250 Adet 15.10 TL
- 1000 Adet 13.22 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 10 mm
Thickness: 1 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Strength: 0-2 kg
Coating: Nickel
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Quality: N35
Certification
Our magnets come with Gauss certification and can be provided t..
9.00 TL
Ex Tax:7.50 TL
- 50 Adet 8.10 TL
- 250 Adet 7.20 TL
- 1000 Adet 6.30 TL
10x1.5 mm Neodymium Disc Magnet
These powerful rare earth magnets are difficult to separate when joined together. This strong neodymium magnet, measuring 10 mm x 1.5 mm in disc shape, is available for bulk purchase.
It has multiple applications including whiteboard mounting, photo/note attachmen..
9.50 TL
Ex Tax:7.92 TL
- 50 Adet 8.55 TL
- 250 Adet 7.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 6.65 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 10 mm
Thickness: 2 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Strength: 0-3 kg
Coating: Nickel
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Quality: N35
Certification
Our magnets come with Gauss certification and can be provided t..
10.00 TL
Ex Tax:8.33 TL
- 50 Adet 9.00 TL
- 250 Adet 8.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.00 TL
Small Neodymium Magnet - D10x3 mm
Small neodymium magnets possess high magnetic attraction despite their size. Our N35 grade neodymium magnets maintain their strength for many years. These round neodymium magnets can be used in hobby experiments, schools, and offices. They can serve as refrigerator..
10.40 TL
Ex Tax:8.67 TL
- 50 Adet 9.36 TL
- 250 Adet 8.32 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.28 TL
D10x5 mm Round Cylindrical Neodymium Magnet N35
The neodymium magnet, also known as a cylinder magnet, D10x5 mm has been enhanced with nickel plating for increased strength. This neodymium magnet has a 10 mm diameter and 5 mm thickness. Despite its compact size, it offers excellent magnetic attract..
14.40 TL
Ex Tax:12.00 TL
- 50 Adet 12.96 TL
- 250 Adet 11.52 TL
- 1000 Adet 10.08 TL
10x10 mm Round Neodymium Magnet N35
Neodymium magnets are resistant to temperatures up to 80 degrees. This 10x10 mm N35 grade neodymium magnet is even stronger with its nickel coating. The cylindrical magnet is designed for use in special projects. With its 10 mm thickness, it can also be used in s..
22.40 TL
Ex Tax:18.67 TL
- 50 Adet 20.16 TL
- 250 Adet 17.92 TL
- 1000 Adet 15.68 TL
10x20 mm N35 Quality Neodymium MagnetThis 10 mm diameter and 20 mm long round cylinder neodymium magnet is nickel plated to make it more durable and long lasting. Nickel plating protects the magnet and makes it stronger at the same time. This magnet, which is much stronger than ferrite magnets, main..
45.00 TL
Ex Tax:37.50 TL
- 100 Adet 36.00 TL
- 500 Adet 32.40 TL
- 2500 Adet 29.25 TL
12x1 mm Round Disc Neodymium Magnet N35Caution: 1 mm thick magnets can easily break when bumped together. Therefore, be careful when separating the magnets. 12 mm in diameter and 1 mm thick, this neodymium magnet is protected by nickel plating. Resistant to 80°C, this thin magnet can be used in your..
10.00 TL
Ex Tax:8.33 TL
- 50 Adet 9.00 TL
- 250 Adet 8.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.00 TL
12 mm Diameter Neodymium Round Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power despite their small size...
10.60 TL
Ex Tax:8.83 TL
- 50 Adet 9.54 TL
- 250 Adet 8.48 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.42 TL
D12x3 mm Round Cylindrical Neodymium Magnet N35
These neodymium magnets, being the strongest magnets in nature, maintain their strength for extended periods. This small magnet with high magnetic attraction can be used in homes as a hobby, schools, homework assignments, projects, and various hand to..
12.96 TL
Ex Tax:10.80 TL
- 50 Adet 11.66 TL
- 250 Adet 10.37 TL
- 1000 Adet 9.07 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 12 mm
Thickness: 5 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Strength: 3-5 kg
Coating: Nickel
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Quality: N35
Certification
Our magnets come with Gauss certification and can be provided t..
16.52 TL
Ex Tax:13.77 TL
- 50 Adet 14.87 TL
- 250 Adet 13.22 TL
- 1000 Adet 11.56 TL
14x2 mm Round Neodymium MagnetThis 14 mm diameter, 2 mm thick round neodymium magnet has a disk structure and can be used in special hobbies. It is preferred in various projects, schools and experiments. The strongest magnet in nature, these neodymium magnets retain their strength for a long time. T..
12.00 TL
Ex Tax:10.00 TL
- 50 Adet 10.80 TL
- 250 Adet 9.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 8.40 TL
15x2 mm Neodymium Magnet (Diameter 15 mm)Round neodymium magnet, nickel plated for increased strength. It is rustproof and liquid resistant. This 2 mm thick magnet is also fragile, so care should be taken not to hit it hard after pulling it apart.This very strong disk neodymium magnet is 15 mm in di..
13.00 TL
Ex Tax:10.83 TL
- 50 Adet 11.70 TL
- 250 Adet 10.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 9.10 TL
15x3 mm Round Neodymium Magnet N35
The 15 mm diameter neodymium magnet has a disc structure and round shape. With its 3 mm thickness, it can be used in specialized hobbies. It's preferred for various projects, schools, and experiments. These neodymium magnets, being the strongest magnets in nature,..
13.50 TL
Ex Tax:11.25 TL
- 50 Adet 12.15 TL
- 250 Adet 10.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 9.45 TL
15x5 mm Neodymium Disc Magnet
This magnet, measuring 15 mm in diameter and 5 mm in thickness, has been strengthened through nickel plating. Neodymium magnets, known as permanent magnets, retain their magnetic properties for extended periods. Much stronger than ferrite magnets, they maintain their s..
27.14 TL
Ex Tax:22.62 TL
- 50 Adet 24.43 TL
- 250 Adet 21.71 TL
- 1000 Adet 19.00 TL
15x10 mm Powerful Neodymium Magnet
This neodymium magnet, measuring 15 mm in diameter and 10 mm in thickness, possesses an extremely powerful structure. Its strength has been further enhanced through nickel plating. It features a triple-layer Ni-Cu-Ni coating. Nickel-plated neodymium magnets are si..
53.10 TL
Ex Tax:44.25 TL
- 100 Adet 42.48 TL
- 500 Adet 38.23 TL
- 2500 Adet 34.52 TL
15 mm Diameter Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets of 15x15 mm size are rare-earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field properties. These magnets are made from an NdFeB compound consisting of neodymium, iron, and boron. Despite their small size, 15x15 mm neodymium magnets offer remarkable mag..
50.00 TL
Ex Tax:41.67 TL
- 100 Adet 40.00 TL
- 500 Adet 36.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 32.50 TL
15x20 mm N35 Quality Neodymium MagnetThis very strong round cylinder neodymium magnet with a diameter of 15 mm and a length of 20 mm is nickel plated to make it more durable and long lasting. Nickel plating protects the magnet as well as making it stronger. Much stronger than ferrite magnets, this m..
75.00 TL
Ex Tax:62.50 TL
- 25 Adet 63.75 TL
- 100 Adet 56.25 TL
- 500 Adet 48.75 TL
18x3 mm Powerful Neodymium Disc Magnet
The 18 mm diameter neodymium magnet is one of the permanent disc-shaped magnets. Being among the strongest magnets on Earth, neodymium magnets have a high magnetic field. With its 3 mm thickness, it can be used in specialized hobbies. Strengthened through nick..
21.12 TL
Ex Tax:17.60 TL
- 50 Adet 19.01 TL
- 250 Adet 16.90 TL
- 1000 Adet 14.78 TL
Neodymium Disc Curtain Magnet
This curtain magnet, measuring 18 mm in diameter and 3 mm in thickness, is made from neodymium. It can be used as a curtain magnet in homes, cars, caravans, ships, and boats. The neodymium magnet easily secures your curtains to the wall as long as the backing area is m..
32.00 TL
Ex Tax:26.67 TL
- 100 Adet 25.60 TL
- 500 Adet 23.04 TL
- 2500 Adet 20.80 TL
Magnet Specifications
Diameter: 18 mm
Thickness: 5 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Strength: 5-10 kg
Coating: Nickel/Zinc
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Operating Temperature: Max 80°C
Quality: N35
Certification
Our magnets come with Gauss certification and can be prov..
25.92 TL
Ex Tax:21.60 TL
- 50 Adet 23.33 TL
- 250 Adet 20.74 TL
- 1000 Adet 18.14 TL
D20x1.5 mm Round Cylindrical Neodymium Magnet N35Product Description:Neodymium magnets, the strongest type of magnet in nature, maintain their high attraction for a long time. Despite their small size, they create a strong magnetic field. It can be used in hobby projects, homes, schools, homework an..
15.00 TL
Ex Tax:12.50 TL
- 50 Adet 13.50 TL
- 250 Adet 12.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 10.50 TL
Ø20x2 mm Neodymium Magnet
Super strong rare earth magnets are difficult to separate when joined together. This powerful neodymium magnet with a 20 mm (2 cm) diameter might be just what you need.
Perfect for attaching notes to refrigerator doors, securing whiteboards, or joining various steel par..
17.00 TL
Ex Tax:14.17 TL
- 50 Adet 15.30 TL
- 250 Adet 13.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 11.90 TL
Neodymium Disc Magnet - D20x3 mm
The N35 neodymium round magnet, measuring 20 mm in diameter and 3 mm in thickness, can be used in hobby experiments, schools, and offices. While this super-strong neodymium magnet is perfect for hobby purposes, it's also suitable for various projects.
It's a safe..
20.00 TL
Ex Tax:16.67 TL
- 50 Adet 18.00 TL
- 250 Adet 16.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 14.00 TL
Certification and Company Information
Our magnets come with Gauss certification and can be provided to you for an additional fee upon request. Our company provides Gauss measurement and certification services for all magnetic systems. Magneteksan manufactures magnetic equipment and magnets for vari..
35.00 TL
Ex Tax:29.17 TL
- 100 Adet 28.00 TL
- 500 Adet 25.20 TL
- 2500 Adet 22.75 TL
20 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet
20x10 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). The 20x10 mm neodymium magnet possesses permanent power and delivers incredible strength despite it..
68.50 TL
Ex Tax:57.08 TL
- 25 Adet 58.22 TL
- 100 Adet 51.37 TL
- 500 Adet 44.52 TL
22 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet
22x15 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). The 25x15 mm neodymium magnet possesses permanent power and delivers remarkable strength despite..
125.00 TL
Ex Tax:104.17 TL
- 10 Adet 106.25 TL
- 50 Adet 93.75 TL
- 250 Adet 81.25 TL
N45 Neodymium Magnet - 23 mm Diameter, 10 mm Thickness
N45 Grade neodymium magnets, significantly stronger than standard N35 quality, are made from rare earth elements. Our NdFeB (Neodymium Iron Boron) magnets are first-quality products with nickel plating, available exclusively through Mıknatıs AV..
259.00 TL
Ex Tax:215.83 TL
- 5 Adet 233.10 TL
- 25 Adet 207.20 TL
- 100 Adet 181.30 TL
23 mm Diameter N45 Grade Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power despite their small s..
305.00 TL
Ex Tax:254.17 TL
- 5 Adet 274.50 TL
- 25 Adet 244.00 TL
- 100 Adet 213.50 TL
25 mm Diameter Round Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power despite their small si..
35.00 TL
Ex Tax:29.17 TL
- 100 Adet 28.00 TL
- 500 Adet 25.20 TL
- 2500 Adet 22.75 TL
25 mm Diameter Neodymium MagnetThe 25x2.5 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field properties. Composed of neodymium, iron, and boron elements (NdFeB), these magnets offer permanent power and incredible strength despite their small size. They are used in ever..
36.00 TL
Ex Tax:30.00 TL
- 100 Adet 28.80 TL
- 500 Adet 25.92 TL
- 2500 Adet 23.40 TL
25 mm Diameter Round Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power despite their small si..
42.00 TL
Ex Tax:35.00 TL
- 100 Adet 33.60 TL
- 500 Adet 30.24 TL
- 2500 Adet 27.30 TL
25 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet
25x3.5 mm neodymium magnets are rare-earth magnets recognized for their strong magnetic field properties. Composed of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB), these magnets possess permanent strength and deliver remarkable power despite their compact size. They are wide..
43.00 TL
Ex Tax:35.83 TL
- 100 Adet 34.40 TL
- 500 Adet 30.96 TL
- 2500 Adet 27.95 TL
Neodymium Disc Magnet - D25x5 mm
The N35 neodymium round magnet, measuring 25 mm in diameter and 5 mm in thickness, can be used in hobby experiments, schools, and offices. While this super-strong neodymium magnet is perfect for hobby purposes, it's also suitable for various projects.
It's a safe..
55.00 TL
Ex Tax:45.83 TL
- 100 Adet 44.00 TL
- 500 Adet 39.60 TL
- 2500 Adet 35.75 TL
25x10 mm Neodymium Magnet - 25 mm Diameter, 10 mm Thickness
This round disc neodymium magnet offers powerful magnetic attraction with its 25 mm diameter. You can easily use it in your projects, homework, homes, and schools. The product is nickel-plated and N35 grade quality. Nickel-plated products ..
120.00 TL
Ex Tax:100.00 TL
- 10 Adet 102.00 TL
- 50 Adet 90.00 TL
- 250 Adet 78.00 TL
25mm Power Pack: Meet N38 Quality Neodymium Magnet!Small But Powerful: Neodymium magnets are known for their incredible attraction. This 25mm diameter miracle is also powerful enough to surprise you despite its tiny structure!Don't Limit Your Imagination: Neodymium magnets are used in a wide range o..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
Neodymium Very Strong Round Magnet - D28x5 mmThe 28 mm diameter and 5 mm thick N35 neodymium round magnet can be used in hobby experiments, schools and offices. This super strong neodymium magnet is ideal for both hobbyists and projects.This magnet can carry a load of 20-30 kg, so care should be tak..
81.42 TL
Ex Tax:67.85 TL
- 25 Adet 69.21 TL
- 100 Adet 61.07 TL
- 500 Adet 52.92 TL
Neodymium Super Strong Round Magnet - D30x5 mm
The N35 neodymium round magnet, measuring 30 mm in diameter and 5 mm in thickness, can be used in hobby experiments, schools, and offices. While this super-strong neodymium magnet is perfect for hobby purposes, it's also suitable for various projects.
..
119.00 TL
Ex Tax:99.17 TL
- 25 Adet 101.15 TL
- 100 Adet 89.25 TL
- 500 Adet 77.35 TL
30x10 mm Very Strong Round Neodymium MagnetThe 30 mm (3 cm) diameter neodymium magnet is reinforced with nickel plating. This rare earth magnet provides the perfect support for special projects with its very strong structure. Despite its 30x10 mm dimensions, it has a gravitational force of approxima..
190.00 TL
Ex Tax:158.33 TL
- 10 Adet 161.50 TL
- 50 Adet 142.50 TL
- 250 Adet 123.50 TL
N38 Neodymium: The New Name for Power!30mm Power Pack: This nickel-plated 30mm diameter neodymium magnet surpasses the N35 series for those seeking true power. This rare earth magnet will be the ideal power source for your most special projects.Small Size, Big Power: Despite its 30x10 mm size, the N..
275.00 TL
Ex Tax:229.17 TL
- 5 Adet 247.50 TL
- 25 Adet 220.00 TL
- 100 Adet 192.50 TL
N45 Neodymium Magnet - Very StrongThe 30 mm (3 cm) diameter neodymium magnet is nickel plated to increase its strength. Much more powerful than the N35 series, the N45 series is the ideal choice for those who want real power. This very powerful rare earth magnet is the perfect supporter for special ..
358.80 TL
Ex Tax:299.00 TL
- 5 Adet 322.92 TL
- 25 Adet 287.04 TL
- 100 Adet 251.16 TL
30x30 mm Neodymium Magnet - 30 mm Diameter, 30 mm Thickness
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power ..
599.00 TL
Ex Tax:499.17 TL
- 5 Adet 539.10 TL
- 25 Adet 479.20 TL
- 100 Adet 419.30 TL
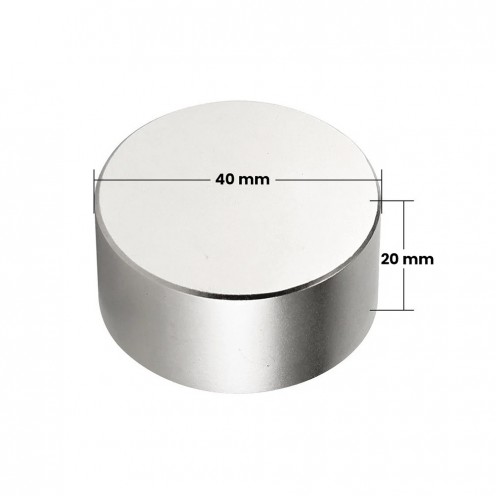
40 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, they deliver incredible power despite their small size. Th..
220.00 TL
Ex Tax:183.33 TL
- 10 Adet 187.00 TL
- 50 Adet 165.00 TL
- 250 Adet 143.00 TL
40 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet
40x10 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). The 40x10 mm neodymium magnet possesses permanent power and delivers incredible strength despite it..
499.00 TL
Ex Tax:415.83 TL
- 5 Adet 449.10 TL
- 25 Adet 399.20 TL
- 100 Adet 349.30 TL
40 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet
40x20 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements). The 40x20 mm neodymium magnet possesses permanent power and delivers remarkable strength despite..
1,099.00 TL
Ex Tax:915.83 TL
- 2 Adet 989.10 TL
- 10 Adet 879.20 TL
- 50 Adet 769.30 TL
50 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet - Extra Strong
The 5 cm diameter neodymium magnet has been enhanced with nickel plating for increased strength. This powerful rare earth magnet is your perfect companion for specialized projects. The 50x5 mm neodymium magnet offers incredible magnetic attraction desp..
499.00 TL
Ex Tax:415.83 TL
- 5 Adet 449.10 TL
- 25 Adet 399.20 TL
- 100 Adet 349.30 TL
D50x10 mm Very Strong Round Neodymium MagnetThis neodymium magnet is 50 mm (5 cm) in diameter and 10 mm (1 cm) thick, and its strength is increased by nickel plating. Despite its small size, it has a very high attraction power. Important points to be considered when using:Push, not pull, the adhesiv..
599.00 TL
Ex Tax:499.17 TL
- 5 Adet 539.10 TL
- 25 Adet 479.20 TL
- 100 Adet 419.30 TL
50x30 mm Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets are made of rare earth elements known for their strong magnetic fields. These magnets are a combination of neodymium, iron and boron and are among the strongest permanent magnets in the world. Despite their small size, neodymium magnets offer extraordinary ..
6%
1,499.00 TL 1,599.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,249.17 TL
- 2 Adet 1,439.10 TL
- 10 Adet 1,279.20 TL
- 50 Adet 1,119.30 TL
50x30 mm Neodymium Magnet - N52 - (4000-6000 Gauss)Neodymium magnets are rare-earth magnets known for their strong magnetic fields. They are made from NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, Boron) components. Among the most powerful permanent magnets in the world, neodymium magnets offer incredible force despite t..
5%
1,899.00 TL 1,999.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,582.50 TL
- 2 Adet 1,799.10 TL
- 8 Adet 1,599.20 TL
- 32 Adet 1,399.30 TL
60 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet - Extra Strong
The 6 cm diameter neodymium magnet has been enhanced with nickel plating for increased strength. This powerful rare earth magnet is your ideal companion for specialized projects. The 60x5 mm neodymium magnet offers incredible magnetic attraction despit..
599.00 TL
Ex Tax:499.17 TL
- 5 Adet 539.10 TL
- 25 Adet 479.20 TL
- 100 Adet 419.30 TL
70 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet - Very Strong
The 70 mm diameter neodymium magnet is nickel plated for increased strength and is the ideal support for very special projects. This 70x5 mm neodymium magnet has an incredible attraction despite its small size. Caution is recommended for large quantity ..
699.00 TL
Ex Tax:582.50 TL
- 2 Adet 629.10 TL
- 10 Adet 559.20 TL
- 50 Adet 489.30 TL
80 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet - Extra Strong
The 8 cm diameter neodymium magnet has been enhanced with nickel plating for increased strength. This powerful rare earth magnet is your ultimate companion for specialized projects. The 80x5 mm neodymium magnet delivers exceptional magnetic attraction ..
799.00 TL
Ex Tax:665.83 TL
- 2 Adet 719.10 TL
- 10 Adet 639.20 TL
- 50 Adet 559.30 TL
90 mm Diameter Neodymium Magnet - Very StrongThis 9 cm diameter neodymium magnet has an increased strength thanks to its nickel coating. With its very strong structure, this rare earth magnet supports you in your special projects. This 90x5 mm neodymium magnet has an incredible attraction despite it..
999.00 TL
Ex Tax:832.50 TL
- 2 Adet 899.10 TL
- 10 Adet 799.20 TL
- 50 Adet 699.30 TL
Magnetic Plate, Customer Videos
You can watch the videos below to learn more about the product and find details about magnetic plate installation. For any questions, you can contact our WhatsApp support line.
Additional Information
Product demonstration videos
Installation guides
..
749.00 TL
Ex Tax:624.17 TL
- 2 Adet 674.10 TL
- 10 Adet 599.20 TL
- 50 Adet 524.30 TL
Magnetic Plate Installation Videos from Our Customers
By watching the videos below, you can learn about the product and find detailed information about magnetic plate installation. For any questions that come to mind, you can reach out to our WhatsApp support line.
Support Information
Det..
999.00 TL
Ex Tax:832.50 TL
- 2 Adet 899.10 TL
- 10 Adet 799.20 TL
- 50 Adet 699.30 TL
Clothing Security Tag Detacher Magnet - 5300 Gauss
The security tag detacher magnet, commonly used in clothing and apparel stores, is composed of powerful multi-pole Neodymium magnets. This clothing security tag detacher with a steel outer casing is primarily preferred in the following areas:
..
478.80 TL
Ex Tax:399.00 TL
- 5 Adet 430.92 TL
- 25 Adet 383.04 TL
- 100 Adet 335.16 TL
Super Strong Clothing Security Tag Detacher Magnet - 15000 Gauss
The security tag detacher magnet, commonly used in clothing and apparel stores, is composed of extremely powerful multi-pole Neodymium magnets. This clothing security tag detacher with a steel outer casing is primarily preferred in th..
6,300.00 TL
Ex Tax:5,250.00 TL
Easy-Mount Table Security Tag Detacher Magnet
The security tag detacher magnet, commonly used in clothing and apparel stores, features powerful multi-pole Neodymium magnets. This clothing security tag detacher with a steel outer casing can be easily mounted to tables or wooden surfaces. It is prima..
1,500.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,250.00 TL
Harddisk Magnet with Special PoleThis hard disk magnet with special polarity is designed for your special projects. This neodymium magnet is a strong magnet and can be used for various projects, homework, at home or in the office.The magnet is glued to a steel base and you can use only the magnet or..
112.00 TL
Ex Tax:93.33 TL
- 25 Adet 95.20 TL
- 100 Adet 84.00 TL
- 500 Adet 72.80 TL
Hard Drive Magnet - Neodymium
The magnet extracted from hard drives is a powerful neodymium type. It's a permanent magnet suitable for various projects, homework assignments, and home or office use.
Versatile Usage
The magnet comes attached to a steel surface, but can be removed and used indepe..
112.00 TL
Ex Tax:93.33 TL
- 25 Adet 95.20 TL
- 100 Adet 84.00 TL
- 500 Adet 72.80 TL
Magnetic Keychain Gift (Without Nameplate)
Please check our other products for models with nameplates or company names. This magnetic keychain can be given as a gift to friends, relatives, or colleagues. Made with special neodymium magnets, it guarantees a pulling force of 2 kg. It creates an attra..
160.00 TL
Ex Tax:133.33 TL
- 10 Adet 136.00 TL
- 50 Adet 120.00 TL
- 250 Adet 104.00 TL
Personalized Magnetic Keychain Gift
The personalized magnetic keychain you are viewing can be given as a gift to your friends, relatives, or colleagues. The product is sent to you with your company name or personal name. Our name-printed magnetic keychains made with special laser processing are per..
200.00 TL
Ex Tax:166.67 TL
- 10 Adet 170.00 TL
- 50 Adet 150.00 TL
- 250 Adet 130.00 TL
It can be used for DNA purification, Protein and cell purification. Known as 96 well magnetic head ..
Teklif İsteyin
- 500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 10000 Adet 0.00 TL
3 mm Long, 2 mm Wide, 1 mm Thick Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets are known as super strong rare earth magnets. Measuring 3x2x1 mm, this small and thin neodymium magnet can be used in sensors and various projects. 1 mm thick, this powerful neodymium magnet is the perfect choice for your custom prod..
3.00 TL
Ex Tax:2.50 TL
- 500 Adet 2.64 TL
- 2500 Adet 2.40 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.10 TL
3 mm Long, 2 mm Wide, 1.5 mm Thick Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets, permanent magnets, are known as super strong rare earth magnets. The small and thin 3x2x1.5 mm neodymium magnet can be used in sensors and various projects. 1.5 mm thick, this powerful neodymium magnet can be ideal for your custom..
3.50 TL
Ex Tax:2.92 TL
- 500 Adet 3.08 TL
- 2500 Adet 2.80 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.45 TL
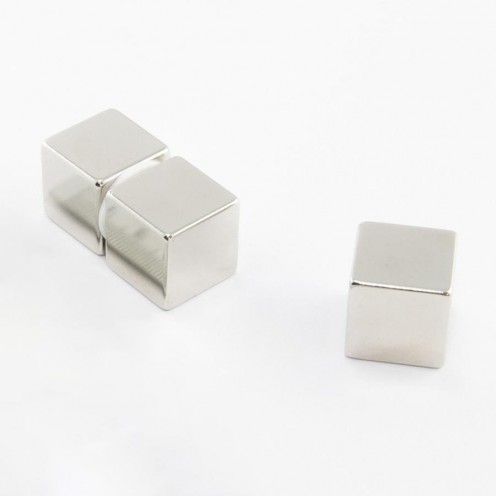
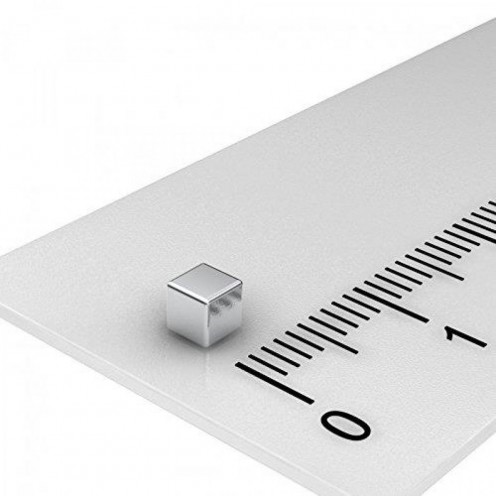
Neodymium Cube Magnet - 3x3x3 mm
This N35 neodymium magnet measures 3x3x3 mm in dimensions. It has been enhanced with nickel plating for increased strength. It features a triple-layer Ni-Cu-Ni coating. Nickel-plated neodymium magnets are significantly stronger and more resistant to environmental fa..
4.00 TL
Ex Tax:3.33 TL
- 500 Adet 3.52 TL
- 2500 Adet 3.20 TL
- 10000 Adet 2.80 TL
4 mm Long, 4 mm Wide, 2.5 mm Thick Neodymium MagnetThe 4 mm square neodymium magnet is specially designed for your hobbies and projects. Despite its small size, it offers a strong magnetic field and completes the missing parts of your projects. Made more durable thanks to nickel plating, this neodym..
4.70 TL
Ex Tax:3.92 TL
- 500 Adet 4.14 TL
- 2500 Adet 3.76 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.29 TL
5 mm Square Neodymium Magnet
5x5x1.5 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (neodymium, iron, and boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, neodymium magnets offer incredible power despite thei..
5.00 TL
Ex Tax:4.17 TL
- 500 Adet 4.40 TL
- 2500 Adet 4.00 TL
- 10000 Adet 3.50 TL
Cube Neodymium Magnet - 5x5x5 mm for Wooden and Wall Board Hobby Use
The N35 neodymium cube magnet can be used for attaching notes and photographs to boards and panels. It's suitable for hobby experiments, schools, and offices. This board magnet, also known as a cube neodymium magnet, can be used f..
6.00 TL
Ex Tax:5.00 TL
- 50 Adet 5.40 TL
- 250 Adet 4.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 4.20 TL
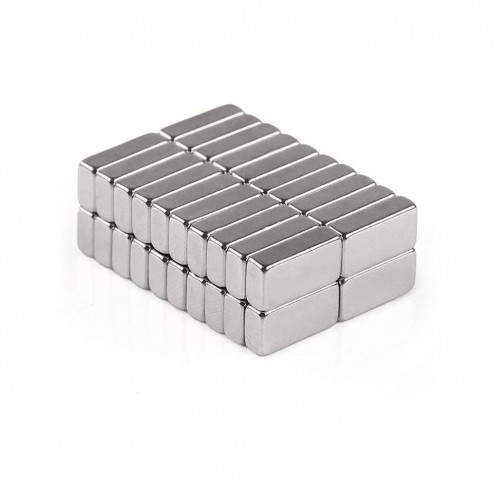
216 Adet 5 mm Küp Neodyum Mıknatıs
N35 neodyum küp mmıknatıs, tahtalarda, panolarda not, fotoğraf yapıştırmak için kullanılabilir. Hobi amaçlı deneylerde, okullarda, ofislerde kullanılabilir. Küp neodyum mıknatıs olarak da geçen bu pano mıknatısı hobi amaçlı tercih edileceği gibi projelerde de..
699.00 TL
Ex Tax:582.50 TL
- 2 Adet 629.10 TL
- 10 Adet 559.20 TL
- 50 Adet 489.30 TL
Technical Specifications
Width: 10 mm
Length: 4 mm
Thickness: 2 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Grade: N35
Operating Temperature: Max. 80°C
Coating: Nickel/Zinc
Strength: 0-250 g
Certification and Manufacturing
Our magnets are Gauss ..
7.50 TL
Ex Tax:6.25 TL
- 50 Adet 6.75 TL
- 250 Adet 6.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.25 TL
The 10x8x1,5 rectangular neodymium magnet is made of NdFeB, known as rare earth elements, and provides a strong magnetic field. These magnets have a wide range of uses, from audio systems to hard drives, from MRI devices to electric motors. For example, they can be used in many different places, fro..
8.00 TL
Ex Tax:6.67 TL
- 50 Adet 7.20 TL
- 250 Adet 6.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.60 TL
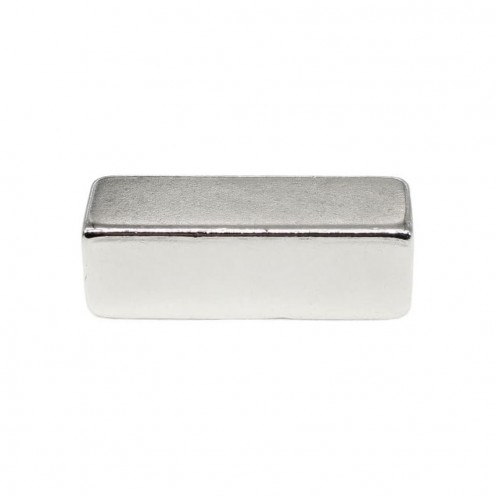
10 mm Rectangular Neodymium Magnet
10x8x2 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They are composed of NdFeB (neodymium, iron, and boron elements). Ranking among the strongest permanent magnets, neodymium magnets deliver incredible strength de..
8.40 TL
Ex Tax:7.00 TL
- 50 Adet 7.56 TL
- 250 Adet 6.72 TL
- 1000 Adet 5.88 TL
Ø10x10x1 mm Neodymium Hobby Magnet
Super strong rare earth magnets are difficult to separate when joined together. This powerful 10 mm x 10 mm square neodymium magnet might be just what you need.
Applications
Can be used for whiteboard mounting or joining various steel parts. Commonly used in h..
10.00 TL
Ex Tax:8.33 TL
- 50 Adet 9.00 TL
- 250 Adet 8.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 7.00 TL
10x10x2 mm Neodymium Magnet
These super-powerful rare earth magnets demonstrate exceptional magnetic strength, making them challenging to separate when connected. The square-shaped neodymium magnet, measuring 10 mm x 10 mm, could be the perfect solution for your magnetic needs.
Uses and Applicat..
12.00 TL
Ex Tax:10.00 TL
- 50 Adet 10.80 TL
- 250 Adet 9.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 8.40 TL
Square Neodymium Magnet 10x10x5 mmNeodymium magnets, which are permanent magnets, are known as super strong rare earth magnets. The small and thin 10x10x5 mm neodymium magnet can be used in sensors and various projects. 5 mm thick, this powerful neodymium magnet can be ideal for your custom producti..
21.00 TL
Ex Tax:17.50 TL
- 50 Adet 18.90 TL
- 250 Adet 16.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 14.70 TL
Cube Neodymium Magnet - Board and Wall Board Magnet 10x10x10 mmThis N35 grade neodymium cube magnet is ideal for sticking notes and photos on boards and clipboards. It can also be used in hobby experiments, schools and offices. This 1x1x1 cm board magnet is also preferred in various projects.Specifi..
28.50 TL
Ex Tax:23.75 TL
- 50 Adet 25.65 TL
- 250 Adet 22.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 19.95 TL
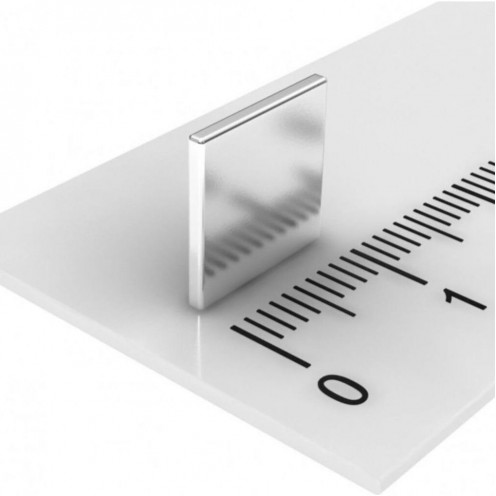
Square Neodymium Magnet 15x1x5 mm
Neodymium magnets, known as super-strong rare earth permanent magnets, offer superior magnetic performance despite their 15 mm dimensions. Made from high-quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy, these magnets possess incredible attractive force relative to their..
16.00 TL
Ex Tax:13.33 TL
- 50 Adet 14.40 TL
- 250 Adet 12.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 11.20 TL
Neodymium magnets, which are among the rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic fields, are composed of NdFeB (neodymium, iron and boron). These magnets, which are extremely powerful despite their small size, have a wide range of uses from audio systems to hard drives, from MRI devices to ..
34.80 TL
Ex Tax:29.00 TL
- 100 Adet 27.84 TL
- 500 Adet 25.06 TL
- 2500 Adet 22.62 TL
15x10x1 mm Thin, Rectangular Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets, known as super-strong rare earth permanent magnets, are challenging to separate when joined together. This powerful neodymium magnet, with its 1 mm thickness, may be essential for your special productions or projects. Its slim profile..
17.40 TL
Ex Tax:14.50 TL
- 50 Adet 15.66 TL
- 250 Adet 13.92 TL
- 1000 Adet 12.18 TL
15x10x3 mm Neodymium N35 Magnet
This N35 grade neodymium magnet measures 15 mm in length, 10 mm in width, and 3 mm in thickness. With its exceptionally high pulling force, this magnet type maintains its strength for many years.
Key Features
High-quality nickel coating
Operates at tem..
18.00 TL
Ex Tax:15.00 TL
- 50 Adet 16.20 TL
- 250 Adet 14.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 12.60 TL
Square Neodymium Magnet 10x10x5 mm Neodymium magnets are known as super strong rare earth magnets. This 10 mm high power square neodymium magnet offers superior magnetic performance. It is made of high quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy and has an incredible attraction for its size. Ide..
27.00 TL
Ex Tax:22.50 TL
- 50 Adet 24.30 TL
- 250 Adet 21.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 18.90 TL
15x15x5 mm Square Magnet - Neodymium Very StrongNeodymium magnets, although small in size, have a very high attraction power. This square magnet you are examining is neodymium and has a size of 15x15x5 mm.This model, known as neodymium magnet or rare earth magnet, must be separated by sliding when i..
32.00 TL
Ex Tax:26.67 TL
- 100 Adet 25.60 TL
- 500 Adet 23.04 TL
- 2500 Adet 20.80 TL
15 mm Square Neodymium Magnet15x15x5 mm neodymium N45 magnets are rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field properties. NdFeB, ie neodymium, consists of iron and boron elements. Neodymium magnets, which are among the most powerful permanent magnets, offer incredible power despite thei..
69.00 TL
Ex Tax:57.50 TL
- 25 Adet 58.65 TL
- 100 Adet 51.75 TL
- 500 Adet 44.85 TL
Rectangular Neodymium Magnet 20x6x2 mm
Neodymium magnets, known as super-strong rare earth permanent magnets, deliver exceptional magnetic performance despite their 20 mm size. Manufactured from high-quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy, these magnets possess remarkable attractive force relat..
20.00 TL
Ex Tax:16.67 TL
- 50 Adet 18.00 TL
- 250 Adet 16.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 14.00 TL
Magnet AVM 20x10x1 mm
Professional-grade neodymium magnet designed for various applications, featuring precise dimensions and reliable performance.
Technical Specifications
Length: 20 mm (1 cm)
Width: 10 mm (1 cm)
Thickness: 1 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Magnet Type: Neodym..
22.00 TL
Ex Tax:18.33 TL
- 50 Adet 19.80 TL
- 250 Adet 17.60 TL
- 1000 Adet 15.40 TL
Rectangular Neodymium Magnet 20x10x1.5 mm
These super-strong rare earth permanent magnets deliver exceptional magnetic performance despite their compact 20 mm size. Manufactured from premium NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy, they offer incredible attractive force relative to their dimensions. The..
22.50 TL
Ex Tax:18.75 TL
- 50 Adet 20.25 TL
- 250 Adet 18.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 15.75 TL
Ø20x10x2 mm Neodymium Magnet
These super-strong rare earth magnets are challenging to separate when joined together. The 20 mm length neodymium magnet might be exactly what you need for your applications. Perfect for whiteboard mounting or joining various steel components. Commonly used in hobby pr..
23.00 TL
Ex Tax:19.17 TL
- 50 Adet 20.70 TL
- 250 Adet 18.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 16.10 TL
Rectangular Block Neodymium Magnet - 20x10x3 mm
Our nickel-coated neodymium magnets offer superior strength and environmental resistance compared to zinc-coated alternatives. This N35 grade 20x10x3 mm magnet is perfect for hobby experiments, schools, and office applications. All our products provid..
23.50 TL
Ex Tax:19.58 TL
- 50 Adet 21.15 TL
- 250 Adet 18.80 TL
- 1000 Adet 16.45 TL
20x10x5 mm Super Strong Neodymium Magnet
These super-powerful rare earth magnets are exceptionally strong and challenging to separate when joined together. At 2 cm in length, this super-strong neodymium magnet offers approximately 15 kg of pulling force. To separate attached magnets, simply slide t..
30.00 TL
Ex Tax:25.00 TL
- 100 Adet 24.00 TL
- 500 Adet 21.60 TL
- 2500 Adet 19.50 TL
Very Strong N52 Neodymium Magnet - Length 20 mm, Width 10 mm, Thickness 5 mmMuch stronger than a standard neodymium magnet, the N52 magnet is designed for your special projects. Our product is nickel plated, making it more durable and long-lasting. Nickel plating protects the magnet and makes it str..
70.00 TL
Ex Tax:58.33 TL
- 25 Adet 59.50 TL
- 100 Adet 52.50 TL
- 500 Adet 45.50 TL
20x15x5 mm Neodymium Rectangular Magnet
These rare earth neodymium magnets maintain their magnetic properties for extended periods. Measuring 20 mm (2 cm) in length, 15 mm (1.5 mm) in width, and 5 mm (0.5 cm) in thickness, these nickel-coated magnets are significantly stronger than ferrite magnets...
41.12 TL
Ex Tax:34.27 TL
- 100 Adet 32.90 TL
- 500 Adet 29.61 TL
- 2500 Adet 26.73 TL
Door Magnet for Home, Caravan, Office, Car - 20x15x5 mm
Our domestically manufactured door magnet is perfect for homes, caravans, and off-road vehicles. This door retention magnet is ideal for bar doors and double-swing doors, effectively reducing door movement and providing stable positioning.
..
Teklif İsteyin
- 500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 10000 Adet 0.00 TL
20x20x5 mm Powerful Neodymium Magnet
Despite their compact size, neodymium magnets possess exceptional pulling force. This 20x20x5 mm neodymium magnet demonstrates remarkable strength while maintaining a slim profile. Due to their inherent structure, these magnets are relatively fragile, so avoid l..
54.00 TL
Ex Tax:45.00 TL
- 100 Adet 43.20 TL
- 500 Adet 38.88 TL
- 2500 Adet 35.10 TL
Super Strong Neodymium Cube Magnet 20x20x20 mm
This N35 grade product is designed for your hobbies and projects. Its special coating provides enhanced environmental resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 80°C. Due to its extreme strength, keep away from children and exercise caution when s..
234.82 TL
Ex Tax:195.68 TL
- 10 Adet 199.60 TL
- 50 Adet 176.11 TL
- 250 Adet 152.63 TL
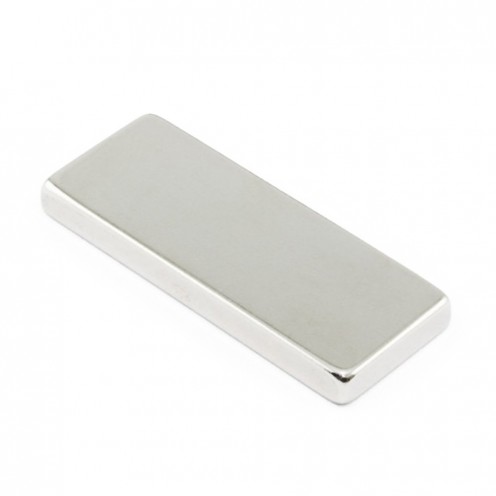
Rectangular Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets, permanent magnets, are known as super strong rare earth magnets. Our high-power neodymium rectangular magnet offers superior magnetic performance despite its 24 mm dimensions. Made of high quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy, these magnets have a..
59.00 TL
Ex Tax:49.17 TL
- 100 Adet 47.20 TL
- 500 Adet 42.48 TL
- 2500 Adet 38.35 TL
25x10x5 mm Super Powerful Neodymium Magnet
The super powerful rare earth magnets are very difficult to separate once they have been joined together. This 25mm long neodymium magnet provides you with approximately 20 kg of pulling power. When the magnets are stuck together, simply push the top mag..
60.00 TL
Ex Tax:50.00 TL
25x20x5 Rectangular Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field properties. They consist of NdFeB, which means neodymium, iron, and boron elements. Neodymium magnets, among the strongest permanent magnets, offer incredible power despite their ti..
124.90 TL
Ex Tax:104.08 TL
- 10 Adet 106.16 TL
- 50 Adet 93.67 TL
- 250 Adet 81.18 TL
25x20x10 mm Neodymium Magnet - Super Strong - Rectangular
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic fields. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron), they offer incredible strength despite their small size. These permanent magnets are used in various applicati..
134.90 TL
Ex Tax:112.42 TL
- 10 Adet 114.67 TL
- 50 Adet 101.18 TL
- 250 Adet 87.69 TL
Neodymium Block Very Strong Magnet - 25x25x5 mmDespite its small size, this square neodymium magnet has a very high attraction force and should be handled with care. 25 mm wide, 25 mm long and 5 mm thick, this magnet can be used to fasten various materials. It is made of neodymium, the strongest typ..
130.00 TL
Ex Tax:108.33 TL
- 10 Adet 110.50 TL
- 50 Adet 97.50 TL
- 250 Adet 84.50 TL
N52 Neodymium Magnet - Very StrongNeodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field properties. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, Boron) alloy, they are among the strongest permanent magnets. Despite their small size, they offer incredible gravity and are used in many ..
139.00 TL
Ex Tax:115.83 TL
- 10 Adet 118.15 TL
- 50 Adet 104.25 TL
- 250 Adet 90.35 TL
30 mm N42 Neodymium MagnetThe 30x6x6 mm neodymium magnets are known as rare earth magnets, renowned for their strong magnetic field properties. These magnets are composed of neodymium, iron, and boron elements (NdFeB). Among the most powerful permanent magnets, neodymium magnets offer incredible str..
63.00 TL
Ex Tax:52.50 TL
- 25 Adet 53.55 TL
- 100 Adet 47.25 TL
- 500 Adet 40.95 TL
Nickel Coated Neodymium Rectangular Magnet 30x10x1 mm
This 1 mm thick magnet features a nickel coating, which not only enhances durability but also provides significantly stronger magnetic properties compared to zinc-coated alternatives. It's important to note that magnets with 1-2 mm thickness are..
32.00 TL
Ex Tax:26.67 TL
- 100 Adet 25.60 TL
- 500 Adet 23.04 TL
- 2500 Adet 20.80 TL
Grid Magnet AVM 30x10x2 mm Technical Details
Length: 30 mm (3 cm)
Width: 10 mm (1 cm)
Thickness: 2 mm
Tolerance: ± 0.1 mm
Magnet Type: Neodymium
Grade: N35
Operating Temperature: Max. 80°C
Coating: Nickel/Zinc
Force: 10-20 kg
Certification and Serv..
34.00 TL
Ex Tax:28.33 TL
- 100 Adet 27.20 TL
- 500 Adet 24.48 TL
- 2500 Adet 22.10 TL
Rectangular Neodymium Magnet 30x10x2.5 mmNeodymium magnets, permanent magnets, are known as super strong rare earth magnets. Despite its 30 mm dimensions, this high-powered rectangular neodymium magnet offers superior magnetic performance and is made of high-quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) allo..
34.50 TL
Ex Tax:28.75 TL
- 100 Adet 27.60 TL
- 500 Adet 24.84 TL
- 2500 Adet 22.43 TL
30x10x3 mm Rectangular Neodymium Block Magnet N35
The neodymium magnet measures 30 mm in length x 10 mm in width x 3 mm in thickness and features a block structure. With its 3 mm thickness, it's suitable for specialized hobbies. It's commonly used in various projects, schools, and experiments. Bein..
36.00 TL
Ex Tax:30.00 TL
- 100 Adet 28.80 TL
- 500 Adet 25.92 TL
- 2500 Adet 23.40 TL
30x10x5 mm Rectangular Neodymium Magnet N35 Grade
This neodymium magnet, measuring 30 mm in length x 10 mm in width x 5 mm in thickness, is manufactured as a super-strong magnet. Enhanced with nickel coating, this magnet is ideal for specialized projects. It's frequently used in schools and experim..
40.00 TL
Ex Tax:33.33 TL
- 100 Adet 32.00 TL
- 500 Adet 28.80 TL
- 2500 Adet 26.00 TL
N52 Neodymium Magnet - Ultra Strong
Neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. They consist of NdFeB (neodymium, iron, and boron elements). Despite their small size, neodymium magnets, among the strongest permanent magnets, offer incredible power. T..
129.00 TL
Ex Tax:107.50 TL
- 10 Adet 109.65 TL
- 50 Adet 96.75 TL
- 250 Adet 83.85 TL
The 30x10x10 mm rectangular neodymium magnet is made of NdFeB, known as rare earth elements, and provides a strong magnetic field. These magnets have a wide range of uses, from audio systems to hard drives, from MRI devices to electric motors. For example, they can be used in many different places, ..
50.00 TL
Ex Tax:41.67 TL
- 100 Adet 40.00 TL
- 500 Adet 36.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 32.50 TL
Very Strong N52 Neodymium Magnet 30x15x10 mmNeodymium magnets are known as super strong rare earth magnets. Our high-power N52 neodymium square magnet offers superior magnetic performance despite its 30 mm dimensions. Made from high quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy, these magnets have an i..
149.00 TL
Ex Tax:124.17 TL
- 10 Adet 126.65 TL
- 50 Adet 111.75 TL
- 250 Adet 96.85 TL
Super Strong Neodymium Magnet - 30x20x5 mmN35 neodymium rectangular magnet can be used in hobby experiments, schools, offices. This super strong neodymium magnet can be used for hobby purposes as well as in projects. This powerful magnet with a gravity of 10-20 kg offers high gravity despite it..
70.00 TL
Ex Tax:58.33 TL
- 25 Adet 59.50 TL
- 100 Adet 52.50 TL
- 500 Adet 45.50 TL
30x20x10 Rectangular Neodymium Magnet
Neodium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field property. NdFeB consists of the elements neodium, iron and boron. Ne Decium magnets, which are among the strongest permanent magnets, offer incredible strength despite their very..
135.00 TL
Ex Tax:112.50 TL
Ultra Strong Neodymium Magnet 30x25x10 mm
Neodymium magnets, permanent magnets known as super strong rare earth magnets, offer superior magnetic performance despite their 30 mm dimensions. Made from high-quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) alloy, these magnets possess incredible attractive force r..
145.00 TL
Ex Tax:120.83 TL
- 10 Adet 123.25 TL
- 50 Adet 108.75 TL
- 250 Adet 94.25 TL
The 35x10x10 mm rectangular neodymium magnet is made of NdFeB, known as rare earth elements, and provides a strong magnetic field. These magnets have a wide range of uses, from audio systems to hard drives, from MRI devices to electric motors. For example, they can be used in many different places, ..
99.00 TL
Ex Tax:82.50 TL
- 25 Adet 84.15 TL
- 100 Adet 74.25 TL
- 500 Adet 64.35 TL
Neodymium Ultra Strong Rectangular Magnet - 40 mm Length, 10 mm Width, 5 mm Thickness
If you're looking for a 40 mm neodymium magnet and the length suits your needs, you can purchase this ultra-strong magnet. It's an N35 grade neodymium block magnet. Suitable for hobby experiments, schools, and off..
50.00 TL
Ex Tax:41.67 TL
- 100 Adet 40.00 TL
- 500 Adet 36.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 32.50 TL
40x10x10 mm Ultra Strong Neodymium Bar Magnet
This 40 mm long neodymium magnet features nickel coating and impact resistance. Its 10x10 mm base dimensions enhance its strength. Every 10 mm thick neodymium magnet possesses exceptional power. This bar-shaped magnet will fully meet your requirements. ..
85.00 TL
Ex Tax:70.83 TL
- 25 Adet 72.25 TL
- 100 Adet 63.75 TL
- 500 Adet 55.25 TL
Neodymium Super Strong Rectangular Magnet - 40mm Length, 15mm Width, 5mm Thickness
This rectangular neodymium magnet has an average pulling force of 30 kg. You can easily use it in your projects. The product is nickel-plated and N35 grade. Nickel-plated products are stronger and more resistant to o..
69.44 TL
Ex Tax:57.87 TL
- 25 Adet 59.02 TL
- 100 Adet 52.08 TL
- 500 Adet 45.14 TL
40x20x5 mm Neodymium Rectangular Magnet
A neodymium magnet measuring 40 mm (4 cm) in length, 20 mm (2 cm) in width, and 5 mm (0.5 cm) in thickness. This magnet, significantly stronger than ferrite magnets, maintains its strength for many years in nature. It's utilized in experiments, schools, motor..
138.00 TL
Ex Tax:115.00 TL
- 10 Adet 117.30 TL
- 50 Adet 103.50 TL
- 250 Adet 89.70 TL
40 mm Rectangular Neodymium MagnetThe 20x5x40 mm neodymium magnets are known for their strong magnetic field properties as rare earth magnets. These magnets consist of neodymium, iron, and boron elements (NdFeB). Despite their small size, neodymium magnets are among the most powerful permanent magne..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
40 mm Rectangular Neodymium MagnetThe 40x5x20 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their strong magnetic field properties. These magnets are composed of neodymium, iron, and boron elements (NdFeB). Among the most powerful permanent magnets, neodymium magnets offer incredible strengt..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
40x20x10 mm Neodymium Magnet - Super Strong - Rectangular
A neodymium magnet measuring 40 mm (4 cm) in length, 20 mm (2 cm) in width, and 10 mm (1 cm) in thickness. This powerful magnet can be used for hobby purposes and various projects. It's ideal for experiments, motor applications, and generati..
176.48 TL
Ex Tax:147.07 TL
- 10 Adet 150.01 TL
- 50 Adet 132.36 TL
- 250 Adet 114.71 TL
A Powerful Magnet at High Temperature: 40x20x10 mm NeodymiumSuperior Performance: With N35 grade resistant up to 150°C, this magnet will not compromise its strength even in high temperature environments.Durable Coating: Nickel plating provides excellent protection against rust and corrosion.Versatil..
399.00 TL
Ex Tax:332.50 TL
- 5 Adet 359.10 TL
- 25 Adet 319.20 TL
- 100 Adet 279.30 TL
High Temperature Resistant Neodymium Magnet - N45 Grade - 150°CNeodymium magnets are known as super strong rare earth magnets. This high power N45 grade neodymium magnet is resistant to high temperature and can work up to 150°C. Much stronger than the N35 grade, the N45 model neodymium magnet is inv..
Teklif İsteyin
- 500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 2500 Adet 0.00 TL
- 10000 Adet 0.00 TL
40x25x5 mm N35 Grade Neodymium Magnet
Despite its slim profile, this neodymium magnet measuring 40 mm (4 cm) in length, 25 mm (2.5 cm) in width, and 5 mm (0.5 cm) in thickness delivers exceptional strength.
Significantly stronger than ferrite magnets, this neodymium magnet maintains its magnetic..
239.00 TL
Ex Tax:199.17 TL
- 10 Adet 203.15 TL
- 50 Adet 179.25 TL
- 250 Adet 155.35 TL
Neodymium Magnet - 40x25x10 mm - Super Strong
This rectangular neodymium magnet features an extremely powerful structure that requires careful handling. Even though neodymium magnets may be small in size, they possess remarkably high magnetic pull force. This particular magnet, measuring 40 mm widt..
285.00 TL
Ex Tax:237.50 TL
- 5 Adet 256.50 TL
- 25 Adet 228.00 TL
- 100 Adet 199.50 TL
Powerful Neodymium Plate Magnet for Drywall Applications
This specialized magnet is perfect for detecting metal areas behind drywall. With its 10mm thickness, it provides effective magnetic pull force. While it can support up to 100 kg when directly attached to a metal surface, this strength reduce..
309.00 TL
Ex Tax:257.50 TL
- 5 Adet 278.10 TL
- 25 Adet 247.20 TL
- 100 Adet 216.30 TL
40x30x4 mm Grid Neodymium Magnet
Our 40x30x4 mm neodymium magnet has a length of 40 mm, a width of 30 mm, and a thickness of 4 mm. The diameter of the holes on the product is 2 mm. The product is nickel-plated, making it more resistant to corrosion. This magnet is much stronger than ferrite magnets..
550.00 TL
Ex Tax:458.33 TL
Neodymium Magnet - Length: 40 mm, Width: 30 mm, Thickness: 10 mm
Our 40x30x10 mm neodymium magnet features dimensions of 40 mm length, 30 mm width, and 10 mm thickness. This nickel-plated product offers enhanced corrosion resistance. Significantly stronger than ferrite magnets, it maintains its mag..
349.00 TL
Ex Tax:290.83 TL
- 5 Adet 314.10 TL
- 25 Adet 279.20 TL
- 100 Adet 244.30 TL
Neodymium Magnet - Length: 50 mm, Width: 10 mm, Thickness: 5 mm
Our powerful rectangular neodymium magnet measures 50 mm in length, 10 mm in width, and 5 mm in thickness. This nickel-plated product offers superior corrosion resistance. Significantly stronger than ferrite magnets, it maintains its m..
138.00 TL
Ex Tax:115.00 TL
- 10 Adet 117.30 TL
- 50 Adet 103.50 TL
- 250 Adet 89.70 TL
Length: 50 mm, Width: 16 mm, Thickness: 4 mm Neodymium Magnet - 200°C High Temperature ResistantOur very strong rectangular neodymium magnet is 50 mm long, 16 mm wide and 4 mm thick. The product is nickel plated and resistant to corrosion. This magnet, which is much stronger than ferrite magnets, re..
499.00 TL
Ex Tax:415.83 TL
- 5 Adet 449.10 TL
- 25 Adet 399.20 TL
- 100 Adet 349.30 TL
Neodymium Magnet - Length: 50 mm, Width: 18 mm, Thickness: 4 mm - Grade B
Our powerful rectangular neodymium magnet measures 50 mm in length, 18 mm in width, and 4 mm in thickness. This nickel-plated product offers enhanced corrosion resistance. Significantly stronger than ferrite magnets, it maint..
259.00 TL
Ex Tax:215.83 TL
- 5 Adet 233.10 TL
- 25 Adet 207.20 TL
- 100 Adet 181.30 TL
Neodymium Magnet - Length: 50 mm, Width: 20 mm, Thickness: 5 mm
Our powerful rectangular neodymium magnet measures 50 mm in length, 20 mm in width, and 5 mm in thickness. This nickel-plated product offers superior corrosion resistance. Significantly stronger than ferrite magnets, it maintains its m..
150.00 TL
Ex Tax:125.00 TL
- 10 Adet 127.50 TL
- 50 Adet 112.50 TL
- 250 Adet 97.50 TL
50x20x10 mm Neodymium MagnetOur very strong rectangular neodymium magnet is 50 mm long, 20 mm wide and 10 mm thick. It is nickel plated and resistant to corrosion. This magnet, which is much stronger than ferrite magnets, maintains its strength for many years in nature. It is used in experiments, sc..
249.00 TL
Ex Tax:207.50 TL
- 5 Adet 224.10 TL
- 25 Adet 199.20 TL
- 100 Adet 174.30 TL
Very Strong Neodymium Magnet - 50x30x10 mmThis super strong neodymium magnet is 50 mm long and 30 mm thick and has a carrying capacity of 150 kg. This nickel plated neodymium magnet is much stronger and more resistant to the external environment than zinc plated ones. The nickel coating makes the ma..
469.60 TL
Ex Tax:391.33 TL
- 5 Adet 422.64 TL
- 25 Adet 375.68 TL
- 100 Adet 328.72 TL
50x50x10 mm Neodymium Magnet (50 mm Length, 10 mm Thickness)This nickel plated neodymium magnet is N35 quality and very strong. Measuring 50x50x10 mm, this magnet can operate in environments up to 80°C.N35 quality magnets are much stronger than lower quality magnets such as N32. Therefore, it offers..
599.00 TL
Ex Tax:499.17 TL
- 5 Adet 539.10 TL
- 25 Adet 479.20 TL
- 100 Adet 419.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
N42 Square Neodymium Magnet Super Strong (100-200 kg)
This nickel-plated neodymium magnet is N42 grade and extremely powerful. With dimensions of 50x50x15 mm, this strong magnet can operate in environments up to 80°C.
Superior Magnetic For..
18%
1,599.00 TL 1,950.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,332.50 TL
- 2 Adet 1,755.00 TL
- 8 Adet 1,560.00 TL
- 32 Adet 1,365.00 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
50x50x15 mm N52 Super Strong Neodymium Magnet
The nickel-plated 50x50x15 mm N52 magnet is composed of neodymium and boron elements. This magnet, possessing incredible power, is also potentially hazardous. When purchasing more than one unit, t..
7%
1,999.00 TL 2,160.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,665.83 TL
- 2 Adet 1,944.00 TL
- 8 Adet 1,728.00 TL
- 32 Adet 1,512.00 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Super Strong Neodymium Magnet 50x50x20 mm
Neodymium magnets, known as super-strong rare earth magnets, offer exceptional magnetic performance despite their compact 50 mm dimensions. Manufactured from high-quality NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) ..
1,599.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,332.50 TL
- 2 Adet 1,439.10 TL
- 10 Adet 1,279.20 TL
- 50 Adet 1,119.30 TL
50x50x25 Neodymium Magnet Super StrongThis 50x50x25 mm nickel plated neodymium magnet has a very strong structure. Produced in N35 quality, this square magnet can operate in environments up to 80°C.Large and very powerful neodymium magnets maintain their health for many years and continue at the sam..
11%
1,699.00 TL 1,920.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,415.83 TL
- 2 Adet 1,728.00 TL
- 8 Adet 1,536.00 TL
- 32 Adet 1,344.00 TL
The 60x20x5 mm rectangular neodymium magnet is made of NdFeB, known as rare earth elements, and provides a strong magnetic field. These magnets have a wide range of uses, from audio systems to hard drives, from MRI devices to electric motors. For example, they can be used in many different places, f..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
60 mm Rectangular Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets with dimensions of 60x25x5 mm are known for their strong magnetic fields as rare earth magnets. Composed of neodymium, iron, and boron, these NdFeB magnets offer incredible strength despite their small size. They are used in a variety of applicatio..
229.00 TL
Ex Tax:190.83 TL
- 10 Adet 194.65 TL
- 50 Adet 171.75 TL
- 250 Adet 148.85 TL
80 mm Rectangular Neodymium MagnetNeodymium magnets with dimensions of 80x25x5 mm are known for their strong magnetic fields as rare earth magnets. Composed of neodymium, iron, and boron, these NdFeB magnets offer incredible strength despite their small size. They are used in a variety of applicatio..
349.00 TL
Ex Tax:290.83 TL
- 5 Adet 314.10 TL
- 25 Adet 279.20 TL
- 100 Adet 244.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
80 mm Length Rectangular Neodymium Magnet
The 80x40x10 mm neodymium magnets are rare earth magnets known for their powerful magnetic field properties. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron elements), these permanent magnets deliver in..
950.00 TL
Ex Tax:791.67 TL
- 2 Adet 855.00 TL
- 10 Adet 760.00 TL
- 50 Adet 665.00 TL
The 80x40x20 mm rectangular neodymium magnet is made of NdFeB, known as rare earth elements, and provides a strong magnetic field. These magnets have a wide range of uses, from audio systems to hard drives, from MRI devices to electric motors. For example, they can be used in many different places, ..
1,299.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,082.50 TL
- 2 Adet 1,169.10 TL
- 10 Adet 1,039.20 TL
- 50 Adet 909.30 TL
Magnetic Gun Holder, Gun MagnetMade of N42 quality very strong neodymium magnet, this gun holder provides 3500 Gauss magnetic field on the surface and 4500 Gauss magnetic field on the magnet surface. It keeps the position of the weapon stable even while moving in your vehicle.Maximum Pulling Force: ..
499.00 TL
Ex Tax:415.83 TL
- 5 Adet 449.10 TL
- 25 Adet 399.20 TL
- 100 Adet 349.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
100x50x20 mm Super Strong Neodymium Magnet
The triple nickel-plated 100x50x20 mm neodymium magnet is extremely powerful and requires careful handling. Its triple-layer coating provides excellent resistance to external conditions. However, acc..
16%
1,999.00 TL 2,400.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,665.83 TL
- 2 Adet 2,160.00 TL
- 8 Adet 1,920.00 TL
- 32 Adet 1,680.00 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
140 mm Length Rectangular Neodymium Magnet
The 140x25x5 mm neodymium magnets are exceptional rare earth magnets renowned for their powerful magnetic field properties. Composed of NdFeB (Neodymium, Iron, and Boron), these magnets deliver remar..
729.00 TL
Ex Tax:607.50 TL
- 2 Adet 656.10 TL
- 10 Adet 583.20 TL
- 50 Adet 510.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Standard Ring NdFeB Neodymium Magnet Ø10xØ5x5 mm
This nickel-plated magnet offers superior strength compared to zinc-coated alternatives, while providing enhanced resistance to environmental conditions and corrosion. With outer diameter 10 mm..
9.00 TL
Ex Tax:7.50 TL
- 50 Adet 8.10 TL
- 250 Adet 7.20 TL
- 1000 Adet 6.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Standard Ring NdFeB Neodymium Magnet Ø15xØ5x5 mm
Available in both countersunk and standard hole versions, this neodymium magnet is perfect for hobby projects, experiments, and various lifting and transport applications. The magnet features a..
30.00 TL
Ex Tax:25.00 TL
- 100 Adet 24.00 TL
- 500 Adet 21.60 TL
- 2500 Adet 19.50 TL
18 mm Diameter Ring Neodymium MagnetThis 18x6x10 mm holed neodymium magnet has a special design with an inner diameter of 6 mm. NdFeB neodymium magnets are classified as permanent and rare earth magnets and are one of the strongest magnet types in the world. Thanks to its 10 mm thickness, it offers ..
25.00 TL
Ex Tax:20.83 TL
- 50 Adet 22.50 TL
- 250 Adet 20.00 TL
- 1000 Adet 17.50 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
18 mm Diameter Ring Neodymium Magnet
The 18x6x10 mm neodymium magnet features a 6 mm inner diameter with unique dimensions. This NdFeB magnet, known as a permanent rare earth magnet, represents the strongest magnetic type found in nature. Wit..
75.00 TL
Ex Tax:62.50 TL
- 25 Adet 63.75 TL
- 100 Adet 56.25 TL
- 500 Adet 48.75 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø20xØ5x10 mm
Available in both countersunk and standard hole versions, this NdFeB neodymium magnet features a 20 mm outer diameter and 5 mm inner diameter. Perfect for hobby projects, experiments, and various lifting and..
86.40 TL
Ex Tax:72.00 TL
- 25 Adet 73.44 TL
- 100 Adet 64.80 TL
- 500 Adet 56.16 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet 20x10x3 mm
This ring-shaped neodymium magnet is specially designed for your custom projects. With an outer diameter of 20 mm, inner diameter of 10 mm, and thickness of 3 mm, it's ideal for hobby projects, experiments, an..
46.08 TL
Ex Tax:38.40 TL
- 100 Adet 36.86 TL
- 500 Adet 33.18 TL
- 2500 Adet 29.95 TL
Perforated Neodymium Magnet 20x12x4 mmThis regular hollow ring neodymium magnet is 20 mm in diameter, 12 mm inside diameter and 4 mm thick. These very strong magnets are difficult to separate when they stick together, so keep them away from children and electronic devices.Instructions for Use:Separa..
48.00 TL
Ex Tax:40.00 TL
- 100 Adet 38.40 TL
- 500 Adet 34.56 TL
- 2500 Adet 31.20 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet 23x6x10 mm
Available in both countersunk and standard hole versions, this 23x6x10 mm neodymium magnet is perfect for hobby projects, experiments, and various lifting and transport applications. This NdFeB magnet features..
130.80 TL
Ex Tax:109.00 TL
- 10 Adet 111.18 TL
- 50 Adet 98.10 TL
- 250 Adet 85.02 TL
N35SH High Temperature Resistant MagnetResistant to 150°C high temperature, this neodymium magnet has a very strong structure. It is designed for your special projects and offered for sale with holes. The 23x6x10 mm N35SH neodymium magnet with normal hole structure is suitable for use in high temper..
598.80 TL
Ex Tax:499.00 TL
- 5 Adet 538.92 TL
- 25 Adet 479.04 TL
- 100 Adet 419.16 TL
Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø23xØ6x20 mm - Very StrongThis neodymium magnet product with ring hole has a carrying power of 40 kg. You can safely use it in special experiments and hobby work. It is widely used in hobby, experiment, various lifting and transportation processes. This NdFeB neodymium magnet h..
249.00 TL
Ex Tax:207.50 TL
- 5 Adet 224.10 TL
- 25 Adet 199.20 TL
- 100 Adet 174.30 TL
N35SH Magnet 150°C Temperature Resistant Very Strong Special Neodymium MagnetProduct Description:The neodymium N35SH magnet with ring hole has the ability to withstand much higher temperatures than standard magnets. This magnet, which can work up to 150 degrees, is produced for special purposes and ..
1,198.80 TL
Ex Tax:999.00 TL
- 2 Adet 1,078.92 TL
- 10 Adet 959.04 TL
- 50 Adet 839.16 TL
25 mm Diameter Ring Neodymium MagnetThis ring neodymium magnet, with dimensions of 25x5x5 mm and an inner diameter of 5 mm, has a unique design. NdFeB neodymium magnets are known as permanent and rare-earth magnets and are among the strongest types of magnets available. With a thickness of 5 mm, it ..
69.00 TL
Ex Tax:57.50 TL
- 25 Adet 58.65 TL
- 100 Adet 51.75 TL
- 500 Adet 44.85 TL
25 mm Diameter Holed Neodymium MagnetThis holed neodymium magnet, with specific dimensions of 25x5x10 mm and an inner diameter of 5 mm, has a unique design. NdFeB neodymium magnets are known as permanent and rare-earth magnets and are among the strongest types of magnets in existence. With a thickne..
109.00 TL
Ex Tax:90.83 TL
- 25 Adet 92.65 TL
- 100 Adet 81.75 TL
- 500 Adet 70.85 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø25x8.5x10 mm
This ring-shaped neodymium magnet features a unique 25 mm diameter design. As a permanent rare earth magnet, this NdFeB magnet represents the strongest magnetic type found in nature. With its 10 mm thicknes..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet 28x8x10 mm
This standard ring neodymium magnet features custom dimensions of 28x8x10 mm, with an outer diameter of 28 mm, inner diameter of 8 mm, and thickness of 10 mm. Due to its exceptional magnetic strength, special ..
199.00 TL
Ex Tax:165.83 TL
- 10 Adet 169.15 TL
- 50 Adet 149.25 TL
- 250 Adet 129.35 TL
Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø28x8.5x10 mmØ28x8.5x10 mm neodymium magnet with ring hole has a special size and is 28 mm in diameter. The NdFeB neodymium magnet is known as a permanent and rare earth magnet and is one of the strongest magnet types in nature. With a thickness of 10 mm, it offers an extremely..
219.00 TL
Ex Tax:182.50 TL
- 10 Adet 186.15 TL
- 50 Adet 164.25 TL
- 250 Adet 142.35 TL
Ø28x8.5x15 mm Neodymium Magnet Ø28x8.5x15 mmThe 28 mm diameter ring hole neodymium magnet has a special gauge. This NdFeB neodymium magnet is known as a permanent and rare earth magnet and is one of the strongest magnet types in nature. With a thickness of 10 mm, it offers an extremely strong attrac..
259.00 TL
Ex Tax:215.83 TL
- 5 Adet 233.10 TL
- 25 Adet 207.20 TL
- 100 Adet 181.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Standard Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø30x9x10 mm
Available in both countersunk and standard hole versions, this NdFeB neodymium magnet features a 30 mm outer diameter and 9 mm inner diameter. With its 10 mm thickness, it provides exceptional magnet..
240.00 TL
Ex Tax:200.00 TL
- 5 Adet 216.00 TL
- 25 Adet 192.00 TL
- 100 Adet 168.00 TL
Normal Delikli NdFeB Neodyum Mıknatıs Ø30x9x20 mm
Havşa delikli olduğu gibi normal delikli neodyum mıknatıs ürünümüz de bulunmaktadır. Hobi, deney, çeşitli kaldırma ve taşıma işlemlerinde kullanılmaktadır. Bu NdFeB neodyum mıknatıs 30 mm çapında ve iç çapı 9 mm boyutundadır. 20 mm kalınlığı ile siz..
352.82 TL
Ex Tax:294.02 TL
- 5 Adet 317.54 TL
- 25 Adet 282.26 TL
- 100 Adet 246.97 TL
30 mm Diameter Ring Neodymium MagnetThis ring neodymium magnet, with dimensions of 30x18x4 mm and an inner diameter of 18 mm, has a unique design. NdFeB neodymium magnets are known as permanent and rare-earth magnets and are among the strongest types of magnets available. With a thickness of 4 mm, i..
99.00 TL
Ex Tax:82.50 TL
- 25 Adet 84.15 TL
- 100 Adet 74.25 TL
- 500 Adet 64.35 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø31x25x4 mm
This custom-sized ring neodymium magnet features a 31 mm outer diameter with unique dimensions. As a permanent rare earth magnet, this NdFeB magnet represents the strongest magnetic type available. Despite it..
109.00 TL
Ex Tax:90.83 TL
- 25 Adet 92.65 TL
- 100 Adet 81.75 TL
- 500 Adet 70.85 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet Ø32x18x6 mm
This specially dimensioned ring neodymium magnet features a 32 mm outer diameter. As a permanent rare earth magnet, this NdFeB magnet represents the strongest magnetic type available. With its 6 mm thickness,..
139.00 TL
Ex Tax:115.83 TL
- 10 Adet 118.15 TL
- 50 Adet 104.25 TL
- 250 Adet 90.35 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Epoxy Coated Neodymium Magnet - AdBlue and Liquid Resistant
Our specialized epoxy-coated magnets are engineered for water resistance and AdBlue compatibility. These N38 grade neodymium magnets are specifically designed for diesel vehicle emis..
217.76 TL
Ex Tax:181.47 TL
- 10 Adet 185.10 TL
- 50 Adet 163.32 TL
- 250 Adet 141.54 TL
40 mm Diameter Ring Neodymium MagnetThis ring neodymium magnet, with dimensions of 40x22x8 mm and an inner diameter of 22 mm, has a unique design. NdFeB neodymium magnets are known as permanent and rare-earth magnets and are among the strongest types of magnets available. With a thickness of 8 mm, i..
329.00 TL
Ex Tax:274.17 TL
- 5 Adet 296.10 TL
- 25 Adet 263.20 TL
- 100 Adet 230.30 TL
Yuvarlak Neodyum Mıknatıs Ø45x38x4 mm
Halka delikli neodyum mıknatıs 45 mm çapında olup özel bir ölçüye sahiptir. Bu NdFeB neodyum mıknatıs daimi ve nadir toprak mıknatısı olarak geçer ve doğadaki en güçlü mıknatıs türüdür. 4 mm kalınlığı ile çok güçlü bir çekim gücü sunar. Bu yüzden çoc..
229.00 TL
Ex Tax:190.83 TL
- 10 Adet 194.65 TL
- 50 Adet 171.75 TL
- 250 Adet 148.85 TL
50 mm Diameter Ring Neodymium MagnetThis ring neodymium magnet, measuring 50x25x8 mm with an inner diameter of 25 mm, has a unique size. NdFeB neodymium magnets are made from permanent and rare earth elements, and are among the strongest types of magnets. With a thickness of 8 mm, it provides a stro..
469.00 TL
Ex Tax:390.83 TL
- 5 Adet 422.10 TL
- 25 Adet 375.20 TL
- 100 Adet 328.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Type Neodymium Magnet - 50 mm Diameter
This specially designed ring neodymium magnet features a 50 mm diameter and represents the pinnacle of magnetic technology. As a permanent rare earth magnet, this NdFeB magnet delivers exceptional m..
1,199.00 TL
Ex Tax:999.17 TL
- 2 Adet 1,079.10 TL
- 10 Adet 959.20 TL
- 50 Adet 839.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Type Neodymium Magnet - 53 mm Diameter
This specialized ring neodymium magnet features a unique 53 mm diameter design. As a permanent rare earth magnet, this NdFeB magnet represents the strongest magnetic type available. Despite its slim..
360.00 TL
Ex Tax:300.00 TL
- 5 Adet 324.00 TL
- 25 Adet 288.00 TL
- 100 Adet 252.00 TL
Neodymium Magnet 60x9x10 mmThis perforated neodymium magnet is shaped like a ring and is made for your special projects. It has 60 mm outer diameter, 9 mm inner diameter and 10 mm thickness. It can be used in hobbies, experiments and various lifting and transportation processes.Our super strong neod..
700.00 TL
Ex Tax:583.33 TL
- 2 Adet 630.00 TL
- 10 Adet 560.00 TL
- 50 Adet 490.00 TL
60 mm Diameter Holed Neodymium MagnetThis holed neodymium magnet, measuring 60x10x10 mm with an inner diameter of 10 mm, has a unique design. NdFeB neodymium magnets are made from permanent and rare earth elements, and are among the strongest types of magnets. With a thickness of 10 mm, it provides ..
549.00 TL
Ex Tax:457.50 TL
- 5 Adet 494.10 TL
- 25 Adet 439.20 TL
- 100 Adet 384.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Neodymium Magnet 60x32x10 mm
This standard ring neodymium magnet features precise dimensions with a 60 mm outer diameter, 32 mm inner diameter, and 10 mm thickness. Its exceptional magnetic strength requires careful handling, particularl..
1,199.00 TL
Ex Tax:999.17 TL
- 2 Adet 1,079.10 TL
- 10 Adet 959.20 TL
- 50 Adet 839.30 TL
Neodymium Magnet with Hole - 70 mm DiameterThe 70 mm diameter ring ring neodymium magnet has a special gauge. This NdFeB neodymium magnet is known as a permanent and rare earth magnet and is one of the strongest magnet types in nature. With a thickness of 10 mm, it offers an extremely strong attract..
1,499.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,249.17 TL
- 2 Adet 1,349.10 TL
- 10 Adet 1,199.20 TL
- 50 Adet 1,049.30 TL
80 mm Diameter Perforated Neodymium MagnetThe 80x32x10 mm neodymium magnet with an inner diameter of 10 mm has a special size. This NdFeB neodymium magnet is known as a permanent and rare earth magnet and is the strongest type of magnet in the world. Thanks to its 10 mm thickness, it provides high a..
899.00 TL
Ex Tax:749.17 TL
- 2 Adet 809.10 TL
- 10 Adet 719.20 TL
- 50 Adet 629.30 TL
90 mm Diameter Perforated Neodymium MagnetThe 90x32x12 mm neodymium magnet with 32 mm inner diameter has a special size. This NdFeB neodymium magnet is known as a permanent and rare earth magnet and is the strongest type of magnet in the world. Its 12 mm thickness ensures high gravitational force. T..
1,099.00 TL
Ex Tax:915.83 TL
- 2 Adet 989.10 TL
- 10 Adet 879.20 TL
- 50 Adet 769.30 TL
100 mm Diameter Perforated Neodymium MagnetThe 100x60x15 mm neodymium magnet with an inner diameter of 100 mm has a special size and is made of very rare earth elements. This neodymium magnet, known as NdFeB, is one of the strongest magnet types in nature and offers an extraordinary attraction thank..
1,299.00 TL
Ex Tax:1,082.50 TL
- 2 Adet 1,169.10 TL
- 10 Adet 1,039.20 TL
- 50 Adet 909.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Ring Type Neodymium Magnet - 120 mm Diameter
This specially dimensioned ring neodymium magnet features a 120 mm outer diameter and 60 mm inner diameter. As a permanent rare earth magnet, this NdFeB magnet represents the strongest magnetic typ..
3,499.00 TL
Ex Tax:2,915.83 TL
- 2 Adet 3,149.10 TL
- 8 Adet 2,799.20 TL
- 32 Adet 2,449.30 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Countersunk Neodymium Magnet - Easy Mounting on Wood, Plastic, Concrete - D10x8/4x5mm
This specially designed countersunk neodymium magnet features a 10 mm diameter with an 8/4 mm inner diameter. The unique countersunk design allows for screw..
23.00 TL
Ex Tax:19.17 TL
- 50 Adet 20.70 TL
- 250 Adet 18.40 TL
- 1000 Adet 16.10 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
12mm Diameter Countersunk Neodymium Magnet
This specially engineered countersunk neodymium magnet allows for screw or bolt installation, enabling secure mounting on non-metallic surfaces. The versatile design makes it perfect for attaching to..
24.00 TL
Ex Tax:20.00 TL
- 50 Adet 21.60 TL
- 250 Adet 19.20 TL
- 1000 Adet 16.80 TL
Countersunk Neodymium Magnet - Easy Installation on Wood, Plastic, ConcreteThis 15 mm diameter countersunk neodymium magnet has an inner diameter of 10/5.5 mm. Measurement values are shown in the product images. The powerful neodymium magnet with a specially produced countersunk hole that can be att..
31.80 TL
Ex Tax:26.50 TL
- 100 Adet 25.44 TL
- 500 Adet 22.90 TL
- 2500 Adet 20.67 TL
15 mm Çap Havşalı Neodyum Mıknatıs - D15x8/4x5mm
15 mm çapında havşalı neodyum mıknatıs iç çapı 8/4 mm değerindedir. Ortasına cıvata, vida takılabilen özel olarak üretilmiş havşa delikli güçlü neodyum mıknatıs. Bu ürün mıknatısı metal olmayan zeminlere tutturmanızı sağlar. Vida sayesinde ahşap, pla..
39.60 TL
Ex Tax:33.00 TL
- 100 Adet 31.68 TL
- 500 Adet 28.51 TL
- 2500 Adet 25.74 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
Countersunk Neodymium Magnet - Easy Mounting on Wood, Plastic, Concrete - D15x10/5.5x5mm
This specialized 15mm diameter countersunk neodymium magnet features a 10/5.5mm inner diameter. Designed for versatile mounting applications, this powerf..
46.00 TL
Ex Tax:38.33 TL
- 100 Adet 36.80 TL
- 500 Adet 33.12 TL
- 2500 Adet 29.90 TL
h2 { font-size: 18px; }
p, ul { font-size: 16px; }
16mm Diameter Countersunk Neodymium Magnet - D16x8/4.2x4 mm
This precision-engineered countersunk neodymium magnet features a 16mm diameter with an 8/4.2mm inner diameter. Specially designed for versatile mounting applications, this powerful ..
46.50 TL
Ex Tax:38.75 TL
- 100 Adet 37.20 TL
- 500 Adet 33.48 TL
- 2500 Adet 30.23 TL
Magnet Types
Magnets are fascinating objects of nature and have some special properties. They generate a magnetic field that can attract or repel certain materials, such as iron and nickel. Because of these properties, they have a wide range of uses in various industrial fields. Magnets are made of different elements and therefore not all magnets are the same. According to their composition and magnetic properties, magnets can be divided into three main categories: permanent magnets, temporary magnets and electromagnets. Each type has its own characteristics.
Very Strong Magnet Types
Neodymium permanent magnets are one of the strongest types of magnets that can maintain their magnetization properties. There are four main types of permanent magnets known: Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB), Samarium Cobalt (SmCo), Alnico and Ceramic or Ferrite. The strongest of these are neodymium magnets. For example, a neodymium magnet with an N35 rating can withstand up to 80°C. You can visit our site to follow the most powerful neodymium magnet models and to examine our perforated, rectangular, countersunk varieties. Our company specializes in this field and offers the features of each product in detail.
Neodymium Magnet Types
Neodymium magnets are powerful magnets formed by the combination of neodymium, one of the rare earth elements, iron and boron. Due to their high magnetic fields and durability, they are used in many industrial applications such as speakers, headphone drivers, motors, generators, hard disk drives, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices, magnetic separators. The main advantage of neodymium magnets is their ability to generate strong magnetic fields despite their small size. However, care must be taken during their use, as these magnets are fragile and their strong magnetic fields can cause serious injury.
Ferrite Magnet Types
Ferrite magnets, also known as oxide magnets, are black in color and come in round and rectangular varieties. They are widely used in sensors, motors and electricity generation. They are preferred in applications requiring high temperatures due to their ability to withstand up to 220°C. Ferrite magnets, although weaker than neodymium, are resistant to high temperatures. They are used in many industrial applications such as loudspeakers, headphone drivers, motors, generators, hard disk drives, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices and magnetic separators. Caution should be exercised during use because these magnets are fragile and their strong magnetic fields can damage electronic devices.